Figure 2. Axial and appendicular skeletal findings.
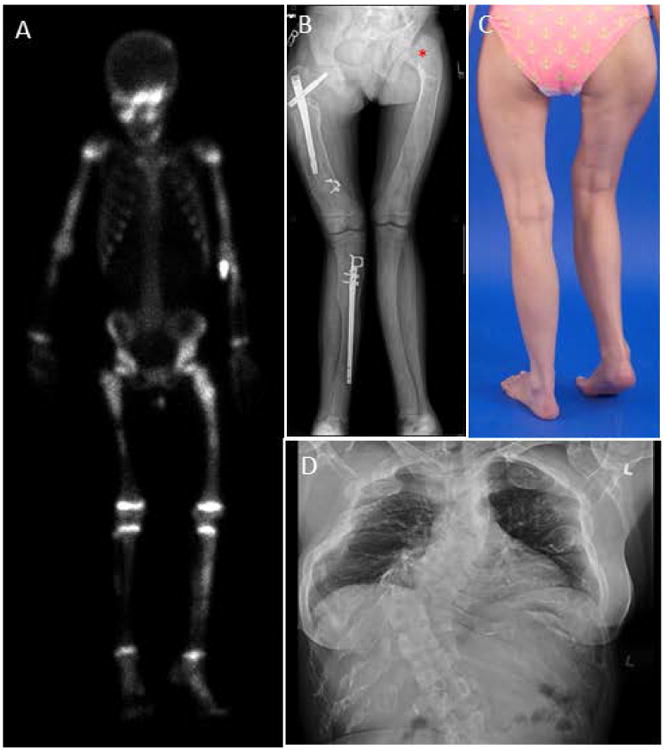
(A) Typical Technetium-99m (99mTc)bone scan, showing uptake in areas of fibrous dysplasia (FD) – including the skull, bilateral arms, legs and pelvis.
(B) Expansion and bowing of the lower extremities in a patient with polyostotic disease. Rods have been placed to help stabilize the right femur and tibia. “Shepherd's crook” deformity can be visualized at the left femoral neck angle (asterisk).
(C) Photograph of a patient with lower extremity deformity and leg-length discrepancy caused by FD.
(D) AP Chest radiograph with severe scoliosis caused by FD of the vertebral column.
