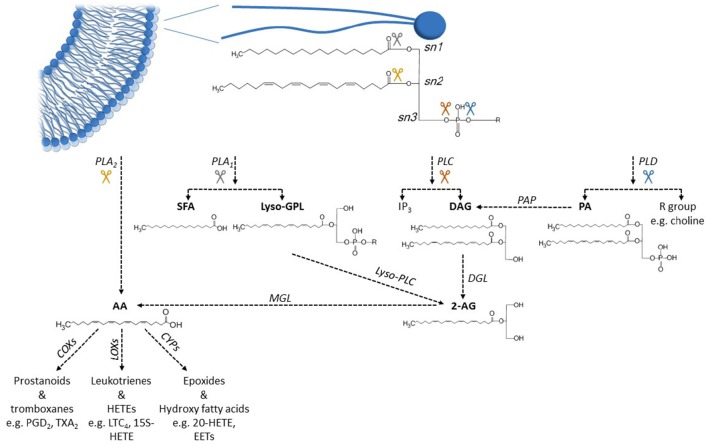
Figure 3.
Metabolic pathways of arachidonic acid hydrolysis and oxidation. Phospholipids in the cell membranes commonly have a SFA esterified to sn1 position and a PUFA, such as arachidonic acid (AA) esterified to sn2 position. Activation of different phospholipases releases AA from phospholipids, either in one enzymatic step (PLA2) or through several enzymatic steps (PLA1, PLC, PLD). Unesterified AA can be further metabolized to various eicosanoid metabolites by different COX, LOX, and CYP enzymes. Abbreviations: 2-AG, 2-arachidonoylglycerol; AA, arachidonic acid; COX, cyclooxygenase; CYP, cytochrome P450 enzyme; DAG, 1,2-diacylglycerol; DGL, DAG lipase; EET, epoxyeicosatrienoic acid; HETE, hydroxyeicosatrienoic acid; IP3, inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate; LOX, lipooxygenase; LTC4, leucotriene C4; Lyso-GPL, lyso-glycerolphospholipid; Lyso-PLC, lysophospholipase C; MGL, monoacylglycerol lipase; PA, phosphatidic acid; PAP, PA phosphatase; PGD2, prostaglandin D2; PLA1, phospholipase A1; PLA2, phospholipase A2; PLC, phospholipase C; PLD, phospholipase D; SFA, saturated fatty acid; TXA2, thromboxane A2.