Figure 1.
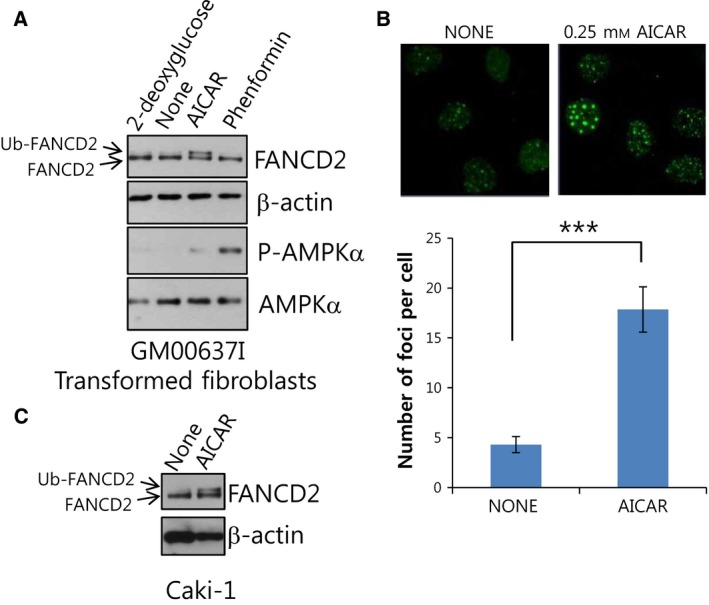
AMPK‐activating AICAR treatment activates FANCD2, a pivotal molecule of Fanconi anemia DNA damage signaling pathway. (A) AICAR treatment induces FANCD2 monoubiquitination in transformed normal fibroblasts (GM00637I). GM00637I cells were treated with 1 mm 2‐deoxyglucose, 0.25 mM AICAR, or 1 mm phenformin for 24 h. Lysates were subjected to western blotting with anti‐FANCD2, phospho‐AMPKα1 (T172), and AMPKα and β‐actin. In FANCD2 blots, the position of monoubiquitinated FANCD2 (Ub‐FANCD2) is indicated by an arrow. (B) AICAR treatment induces formation of FANCD2 nuclear foci in GM00637I fibroblasts. Cells grown on coverslips in 12‐well plates were treated with 0.25 mm AICAR for 24 h. Cells were immunostained with FANCD2 antibody and Alexa 488‐conjugated anti‐rabbit secondary antibody. FANCD2 foci were visualized by confocal microscopy. Representative images are shown at the top. The number of foci per cell was counted and plotted for ≥ 20 cells (bottom panel). The values represent the mean ± SEM (Student's t‐test, ***P < 0.001). (C) AICAR treatment induces FANCD2 monoubiquitination in Caki‐1 cells. Caki‐1 cells were treated with 0.25 mm AICAR for 24 h and monoubiquitination of FANCD2 was monitored as in (A).
