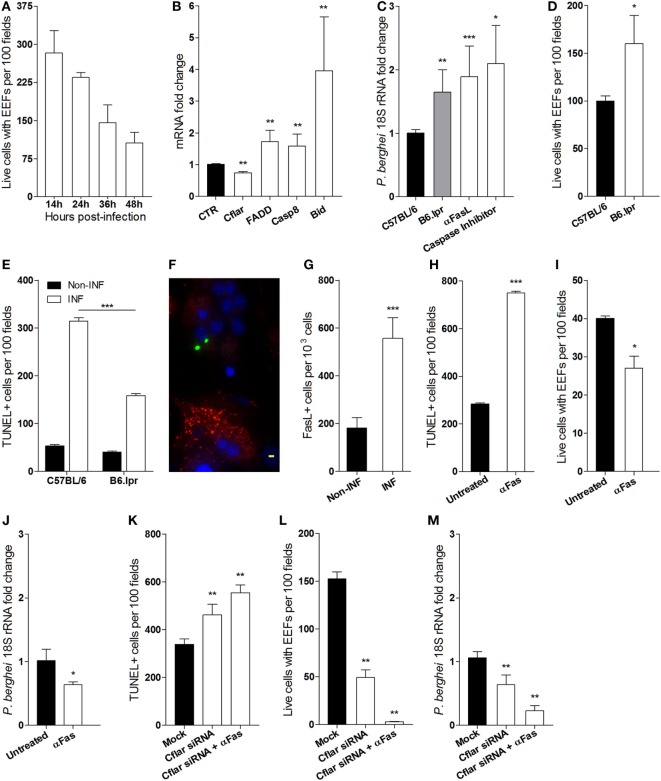
Figure 4.
Fas-mediated hepatocyte apoptosis impairs the success of Plasmodium berghei infection (A) exo-erythrocytic form (EEF)-containing viable hepatocytes were counted at indicated times in infected primary cultures. (B) mRNA quantification of Fas pathway genes at 24 h p.i., relative to non-infected control (CTR) hepatocyte cultures. (C) Parasite yield in infected cultures of Fas-deficient hepatocytes from B6. lpr mice or after blocking Fas pathway with anti-FasL antibody was measured by qRT-PCR of P. berghei 18S rRNA at 40 h p.i. (D) EEF-containing viable hepatocytes of B6. lpr and C57BL/6 mice were counted and (E) the number of apoptotic cells was determined by TUNEL staining in infected and non-infected cultures at 24 h p.i. (F) Representative immunofluorescence image of non-infected hepatocyte expressing FasL (red) in the vicinity of P. berghei-gfp (green) infected hepatocytes [nuclei stained with DAPI (blue)], scale bar—20 µm and (G) counting of FasL-expressing cells in infected and non-infected cultures at 24 h p.i. (H,K) number of apoptotic cells (TUNEL-positive), (I,L) number of viable hepatocytes containing EEFs, and (J,M) parasite yield were measured in primary hepatocyte cultures in the presence or absence of signaling by anti-Fas antibody and/or Cflar siRNA (non-parametric Mann–Whitney test, *p < 0.05, **p ≤ 0.001, and ***p ≤ 0.0001). Data are represented as mean ± SD of triplicate cultures that were performed in at least three independent experiments.