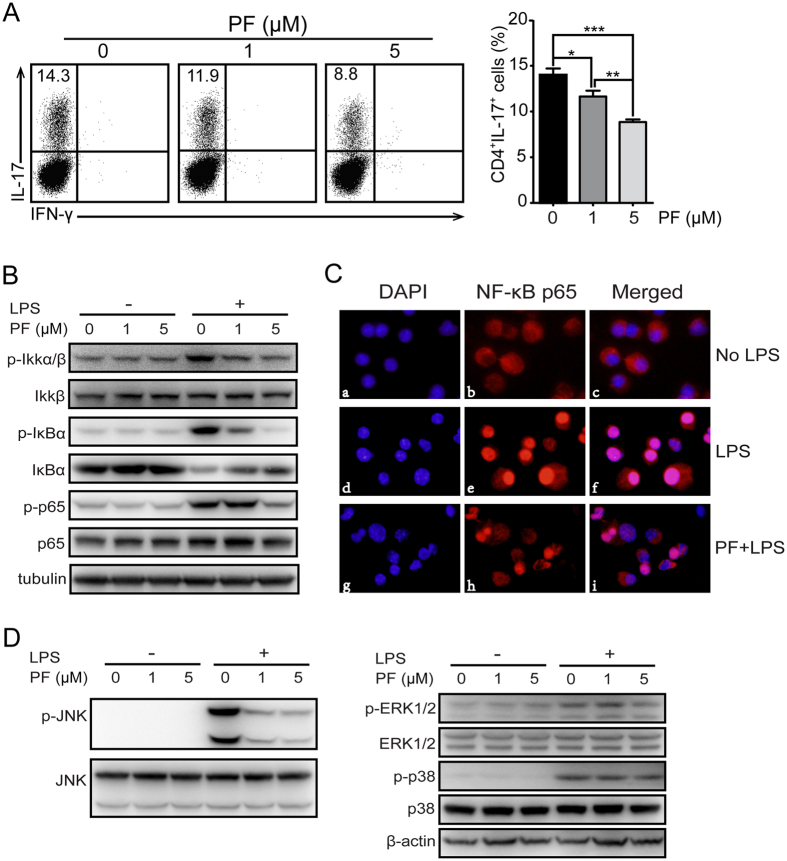
Figure 5. PF inhibited IL-6 production of BMDCs and impaired Th17 cell differentiation via suppressing IKK/NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathway in vitro.
Bone marrow cells from naïve mice were stimulated by GM-CSF and IL-4 to induce DC differentiation in the presence or absence of the indicated concentrations of PF for 5 days, and followed by the stimulation of LPS. (A) The above DCs were co-cultured with naïve CD4+ T cells for Th17 cell differentiation. The percentage of Th17 cells were analyzed by flow cytometry. (B) The protein expression of IKK/NF-κB signaling pathway was analyzed by immunoblot assay. Tubulin served as control. (C) The nucleus translocation of NF-κB-p65 was monitored by fluorescence microscopy (400×). Nuclei were stained in blue; the NF-κB p65 was stained in red. (D) Protein expression of MAPK signaling pathway was detected by immunoblot assay. β-actin was detected as control. Data are representative of three independent experiments. Values were expressed as mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001.