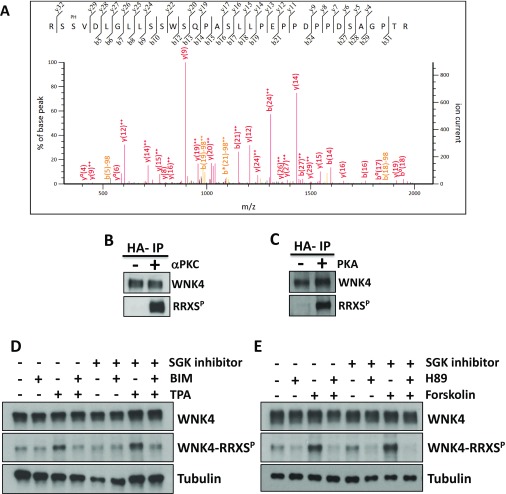
Fig. S1.
WNK4 phosphorylation at RRXS sites. (A) Representative MS/MS spectrum of one of the WNK4 phosphopeptides identified. Specific y and b fragment ions allowed unambiguous identification of the precursor peptide and phosphorylation at specific residues. Fragment ions with neutral loss of phosphate (H3PO4; −98 Da) are indicated (b5–98, etc.). The phosphorylated residue (Ser-64) is indicated with the PH label above the sequence. (B and C) WNK4 is a substrate for in vitro phosphorylation by PKCα and PKA. Kinase inactive WNK4 was purified by immunoprecipitation from extracts of COS-7 cells that were serum-depleted for 12 h before lysis. This decreased the basal WNK4 phosphorylation observed. Immunopurified WNK4 was used as substrate for in vitro phosphorylation by PKCα (B) or PKA (C). WNK4 phosphorylation was assessed by Western blot using the RRXSP antibody. (D and E) The increase in WNK4–RRXS phosphorylation induced by PKC or PKA activation is independent of SGK1 activity. COS-7 cells were transfected with wild-type WNK4 and at 48 h posttransfection, cells were stimulated with the indicated drugs. The SGK1 inhibitor GSK65039, which has been shown to be effective in cell culture experiments (23), was added 30 min before the addition of other drugs. Cells were lysed and extracts were blotted with the indicated antibodies. Similar observations were made in two independent experiments.