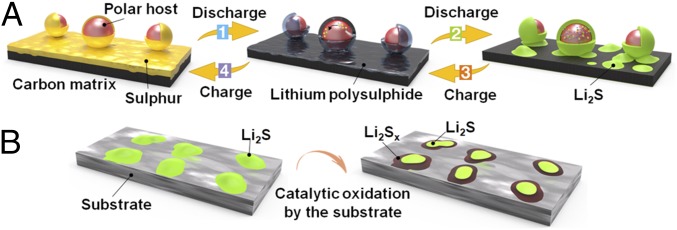
Fig. 1.
Schematic illustration of the sulfur conversion process and the Li2S catalytic oxidation on the surface of the substrate. (A) Sulfur adsorbs on the surface of carbon and polar host and transforms to Li2Sx, which is strongly bonded with the polar host while weakly adsorbed by nonpolar carbon (step 1). Li2Sx transforms to Li2S and is mainly captured by the polar host while isolated islands are deposited on the carbon surface (step 2). (B) The substrate catalyzes Li2S decomposition and favors the oxidization of Li2S to Li2Sx near the substrate surface, and finally to sulfur (steps 3 and 4 in A).