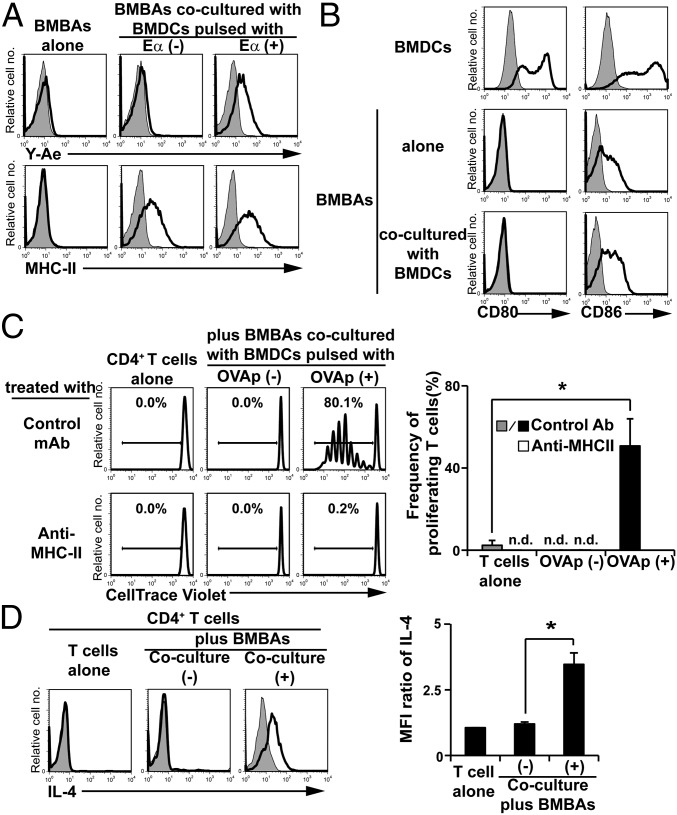
Fig. 4.
Trogocytosis of peptide–MHC-II complexes from DCs confers antigen-presenting ability on basophils. (A) BMBAs were cultured for 12 h with or without BMDCs that had been pulsed with Eα peptide or vehicle (PBS) alone. The expression of MHC-II molecules and processed peptide/MHC-II complexes on BMBAs was detected by using anti-MHC-II and Y-Ae antibodies, respectively. Representative staining profiles are shown. (B) BMBAs were cultured for 12 h with or without BMDCs, and CD80 and CD86 expression on BMBAs was examined in comparison with that on BMDCs. (C) BMBAs were cocultured with BMDCs that had been pulsed with or without OVA peptides. BMBAs were purified from the culture and then cocultured for 5 d with CellTrace Violet-labeled naive CD4+ T cells isolated from the spleen of OT-II Tg mice, in the presence of anti-MHC-II blocking or isotype-matched control Ab. As a control, T cells were cultured without BMDCs. The extent of T-cell proliferation was assessed by dilution of CellTrace Violet. (Left) Representative CellTrace Violet staining profiles. (Right) Frequency (percentage) of divided T cells (showing diluted CellTrace Violet) in each group (mean ± SEM; n = 3 each). (D) BMBAs were cultured with or without BMDCs for 12 h. BMBAs were purified from the culture and then cocultured with naive CD4+ T cells isolated from OT-II Tg mice for 5 d in the presence of OVA peptides as antigens. As a control, T cells were cultured without BMDCs. (Left) IL-4 production of T cells was examined by cytoplasmic staining with anti-IL-4 mAb. (Right) Relative IL-4 staining (mean ± SEM; n = 3 each). Data in A–D are representative of at least three independent experiments. n.d., not detected. *P < 0.05.