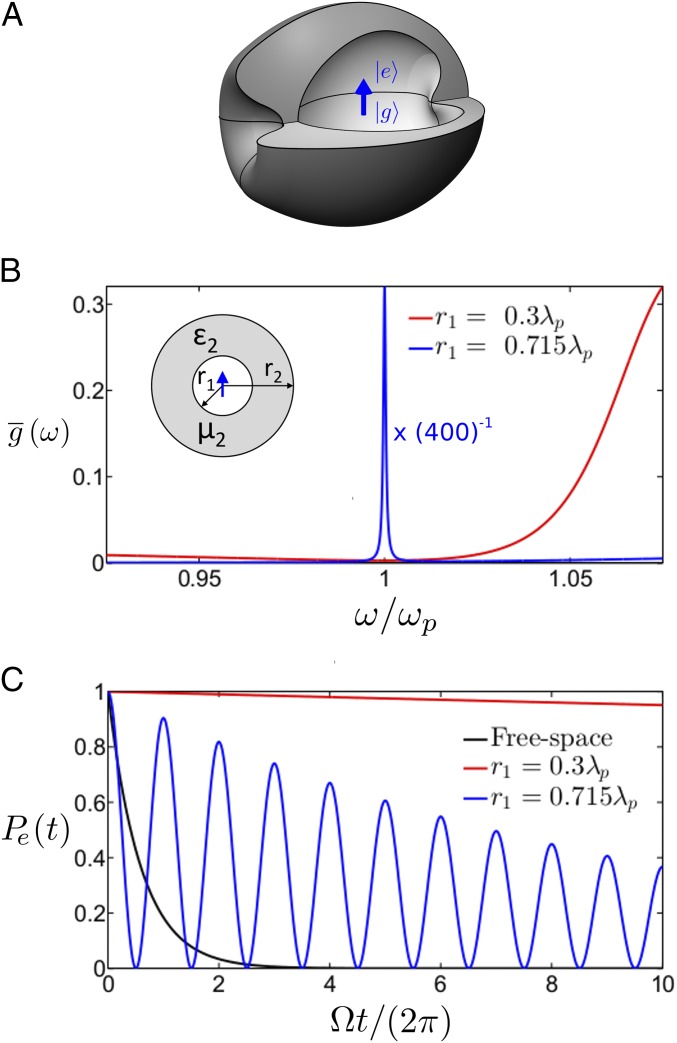
Fig. 2.
Decay dynamics of a quantum emitter (QE) within an ENZ shell. (A) Conceptual sketch of a QE embedded within a macroscopic EMNZ shell of arbitrary shape. (B) Spectral density normalized to its free-space counterpart, for a QE positioned at the center of a spherical shell with external radius , and internal radius of (red) and (blue). The shell is characterized by relative permeability, , and relative permittivity, , with , and (Inset) Sketch of the geometry. (C) Time evolution of the probability of occupation of the excited state, , for nonresonant case of and resonant case of internal radii. For comparison, the black line shows the decay in free space. The magnitude of the transition dipole moment is fixed such that .