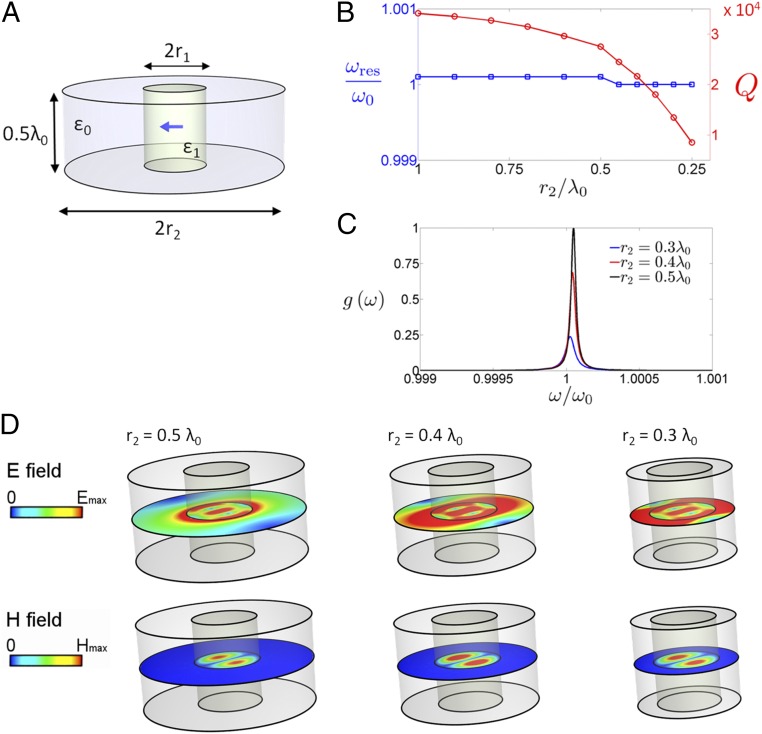
Fig. 4.
Synthetic implementation of ENZ shells as a microwave cylindrical resonator. (A) Geometry of the resonator: cylindrical resonator of height (with arbitrarily chosen value ) and radius , containing a dielectric rod of relative permittivity and whose radius is set to satisfy the resonance condition (). The resonator is bounded by copper walls (). Numerically simulated performance: (B) Eigenfrequency, , and quality factor , as a function of the external radius . (C) Spectral density, , normalized to the maximal computed value, for a QE located at with its dipole moment pointing along for three different external radii. (D) Electric and magnetic field magnitude distributions excited by such QE in the middle plane ().