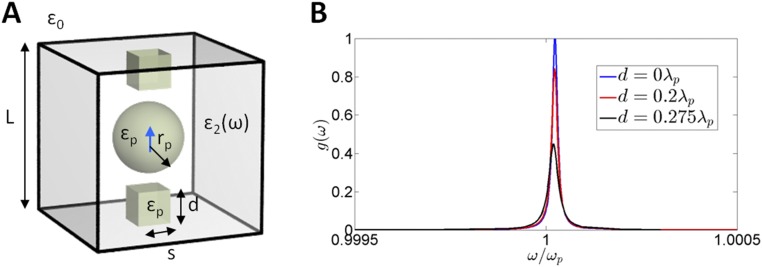
Fig. S2.
Cubic cavity under screw-like deformations. (A) Sketch of the geometry: open cubic cavity of side , immersed in an unbounded vacuum space, containing a dielectric sphere of permittivity and resonant radius , as wells as two “screws” consisting of dielectric blocks of square cross-section with side and variable height . The cavity is otherwise assumed to be filled with a nonmagnetic substance characterized by relative permittivity following a Drude model, with . A QE, modeled as a two-level system whose transition frequency equals the plasma frequency of the host medium filling the cavity, , is positioned at the center of the dielectric sphere. (B) Simulated spectral density, , normalized to the maximal computed value, for different screw heights: (no screws), , and . The figure confirms that screw-like deformations induce no significant detuning but significantly impact the peak value of the spectral density.