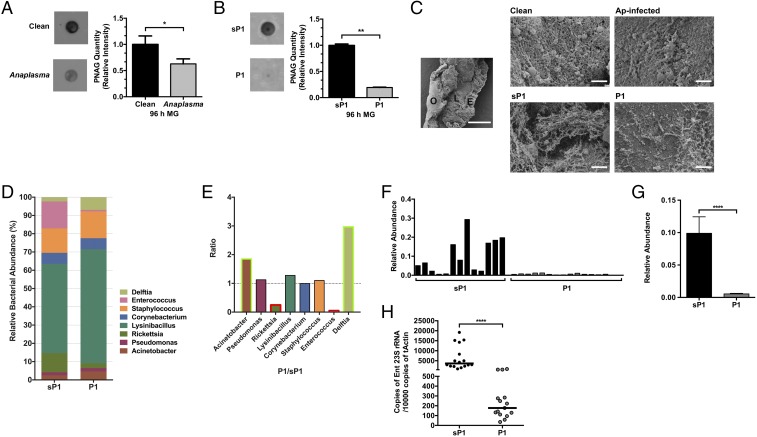
Fig. 4.
IAFGP and P1 alter biofilm formation and microbiota in ticks. (A and B) The relative amount of PNAG extracted from (A) uninfected and. A. phagocytophilum-infected nymphs and (B) P1- vs. sP1-injected nymphs and their respective quantification. Relative intensity of PNAG blots were analyzed by ImageJ (graphs). Graphical data were pooled from two independent experiments, and statistical significance was calculated using a two-tailed nonparametric Mann−Whitney test (**P < 0.01; *P < 0.05). (C) SEM of tick gut biofilm from uninfected (Clean) and A. phagocytophilum (Ap) infected nymphs (Top) and sP1- vs. P1-injected nymphs (Bottom). Representative images are shown for all samples. A representative uninfected (Clean) sample is provided (Left, Middle) at low magnification (500×) to visualize a dissected gut revealing the outside of the gut (O), epithelial cells lining the gut (E), and luminal content (L) (scale bar, 50 μm). Representative images displayed were taken at high magnification (∼8,500×; scale bar, 2 μm) focusing on the luminal content. Ap-infected and P1-injected guts show looser biofilms without dense connecting fibers or matrix-like material associated with reduced biofilms. Clean and sP1 guts, contrastingly, have thicker and well-connected matrix like material with embedded bacteria (cocci) representing robust biofilms. (D and E) Genus level (D) total bacterial composition of sP1- and P1-injected nymphs and (E) fold changes (P1/sP1) of major genera. Green and red box outlines represent genera with increased or decreased abundance in P1-injected nymphs. Statistical significance was calculated using a two-tailed nonparametric Mann−Whitney test (****P < 0.0001). (F–H) Comparison of the levels of Enterococcus species within the tick gut microbiota between sP1- and P1-injected nymphal ticks. (F and G) Relative abundance of Enterococci (F) among individual samples and (G) across all samples (pooled). (H) P1-injected nymphs show reduced levels of Enterococci as determined by qRT-PCR using Enterococci specific primers compared with sP1-injected ticks.