FIGURE 3.
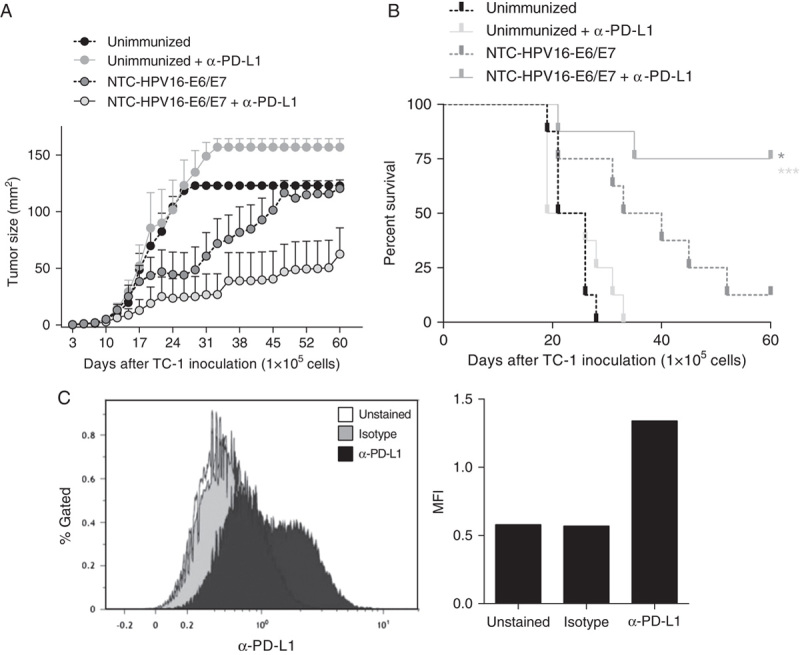
Combination immunotherapy of HPV16-E6/E7 DNA vaccination adjacent to targeting PD-L1 further increases antitumor immunity. A and B, Mice were injected subcutaneously with 1×105 HPV16-E7-expressing TC-1 tumor cells. Seven days after tumor inoculation, mice were immunized 3 times in weekly intervals with NTC-HPV16-E6/E7. Mice received monoclonal antibodies targeting PD-L1 twice weekly after each vaccination, for 3 constitutive weeks. Tumor size was measured and mice were killed when tumor size reached 1 cm3. Shown are mean values of individual tumor sizes (n=8) with SE of mean indicated (A) and percentage of survival (B) over a period of 50 days. C, TC-1 cells were analyzed by flow cytometry for the expression of PD-L1. Shown are histogram and median fluorescent intensity (MFI) of unstained, isotype stained, and α-PD-L1 stained TC-1 cells. *P<0.05, ***P<0.001.
