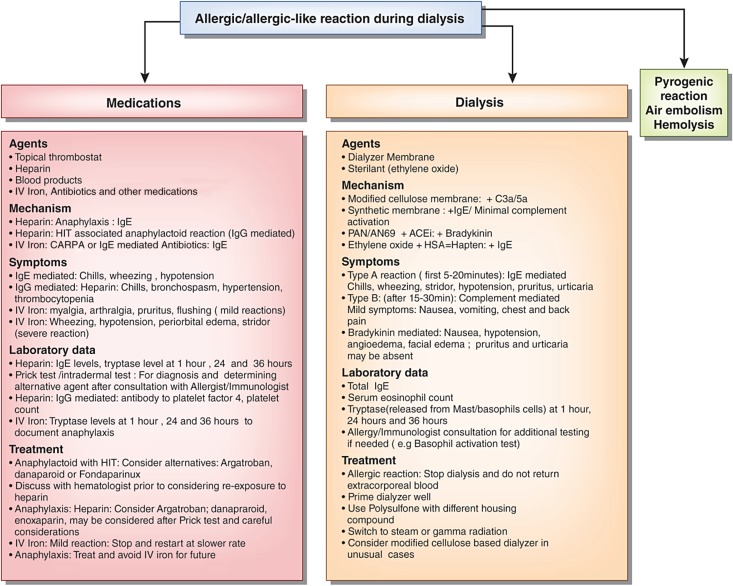
Figure 3.
Flow chart of possible causes of allergic or allergic-like reactions during hemodialysis. Similar symptoms could also be caused by other etiologies, like endotoxin back filtration causing pyrogenic reaction, hemolysis, and rarely, air embolism. Heparin can cause anaphylaxis or anaphylactoid associated with positive heparin–induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) antibodies. Blood products, antibiotics, and other medications used with dialysis may also cause allergic reaction. Intravenous iron may cause a reaction due to IgE-mediated or complement activation–related pseudoallergy (CARPA); at-risk patients have history of atopy, faster infusion, and possible iron dextran exposure than iron sucrose. Ethylene oxide may bind to HSA and act as a hapten to induce an allergic reaction. Although an allergic reaction to synthetic biocompatible dialyzers is rare, it has been reported. A dialyzer with different housing compound or modified cellulose dialyzer may be considered if other causes are ruled out. Occasionally, measuring tryptase and IgE levels may be helpful; additional immunoassays and prick testing may be undertaken after consultation with an allergist. ACEi, angiotensin–converting enzyme inhibitor; AN69, acrylonitrile; HSA, human serum albumin; IV, intravenous; PAN, polyacrylonitrile.