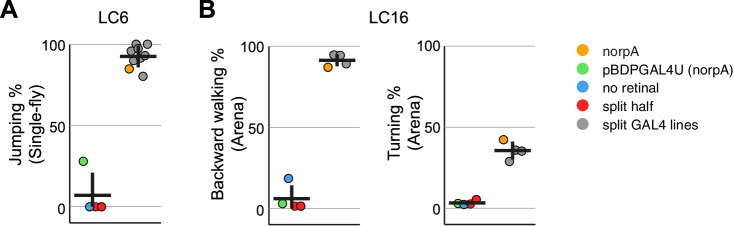
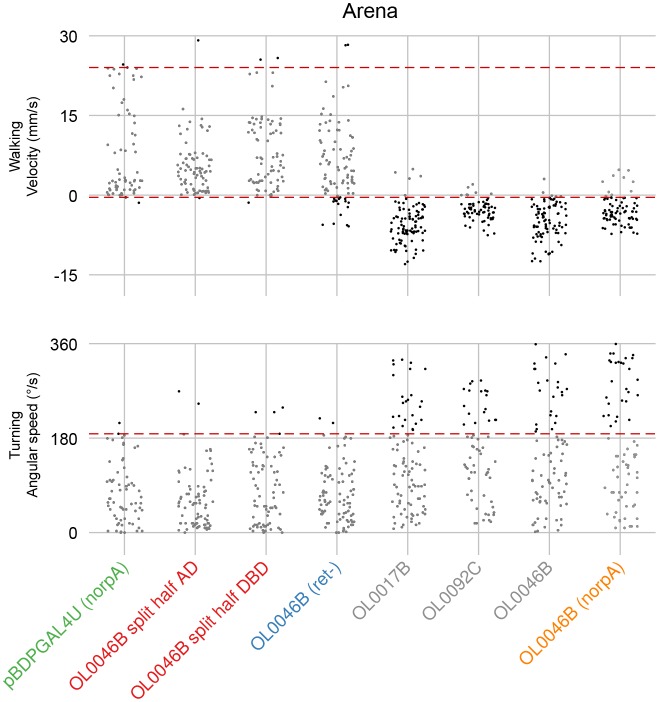
Figure 9. Experiments with additional LC6 and LC16 driver lines confirm the activation phenotypes of these cell types.
(A,B) Behavioral penetrance for different controls and multiple split-GAL4 driver lines for (A) jumping (flies that jumped within 200 ms of stimulation onset) with LC6 controls based on the OL0077B driver line and (B) backward walking and turning with LC16 controls based on the OL0046B driver line. Each dot represents an experiment done with a different genotype: orange, LC neuron activation in blind norpA flies that also carry an LC6 (A) or LC16 (B) split-GAL4 line; green, pBDPGAL4U control in blind norpA flies; blue, flies reared on food without supplemental retinal; red, split-GAL4 DBD or AD halves; grey, genetically distinct split-GAL4 driver lines with targeted expression in LC6 (A) or LC16 (B). Horizontal and vertical lines indicate mean and standard deviation, respectively, for the control group and split-GAL4 group. The genotypes of the driver lines, behavioral penetrance and total trial and fly counts are listed in Supplementary file 1B. Expression patterns of the split-GAL4 driver lines used are shown in Figure 9—figure supplement 1.