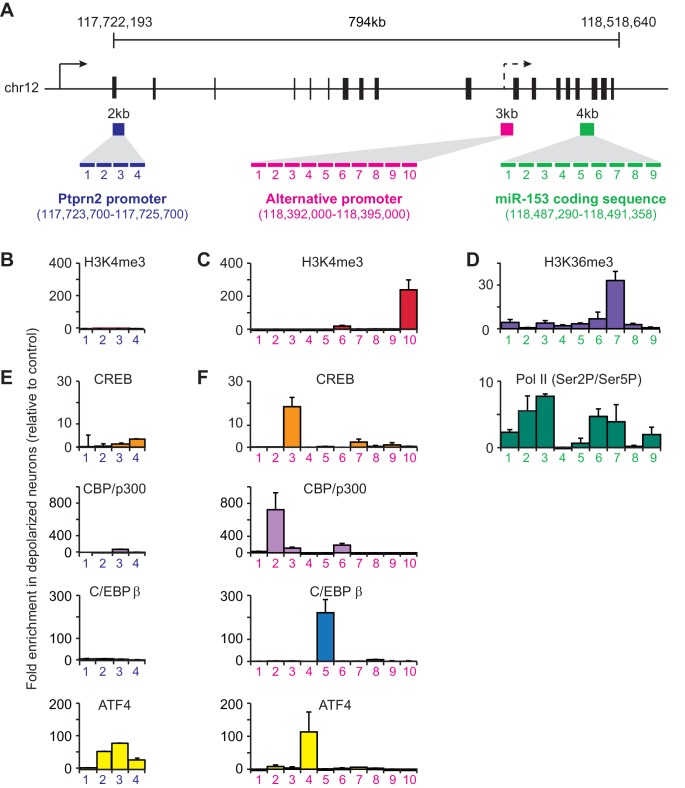
Figure 4. Transcriptional regulation of miR-153 expression may proceed through a cryptic promoter.
(A) Schematic representation of Ptprn2 gene with regions identified for each tiling primer set used to map H3K4me3 for Ptprn2 (purple box, B), H3K4me3 for the cryptic promoter (magenta box, C), and H3K36me3 for the miR-153 coding sequence (green box, D). (B–C) ChIP-qPCR experiments showing changes in the association of histone H3K4me3 (red) with the (B) Ptprn2 promoter and (C) alternative cryptic promoter area. (D) ChIP-qPCR experiments showing changes in association of histone H3K36me3 (purple) and Pol II (green) across the miR-153 coding sequence. Tiling primer sets spanning a 2 kilobase range (1primer set/500 base pairs) were used to map the Ptprn2 promoter (B); a 3 kilobase range (1 primer set/300 base pairs) were used to map the putative cryptic promoter (C); and a 4 kilobase range (1 primer set/440 base pairs) were used to map the miR-153 coding sequence (D). (E–F) ChIP-qPCR experiments showing changes in association of CBP/p300 (purple), CREB (phosphorylated at Ser133, orange), C/EBPß (blue) and ATF4 (yellow) with the (E) Ptprn2 promoter and (F) alternative cryptic promoter area. All experiments were performed with chromatin isolated from mature mouse hippocampal neurons (14 DIV) depolarized continuously for 3 hr with 55 mM KCl relative to untreated hippocampal neurons. The experiments were performed in triplicate and the data are presented as mean ± standard deviation.