Figure 5. SAXS shape reconstructions.
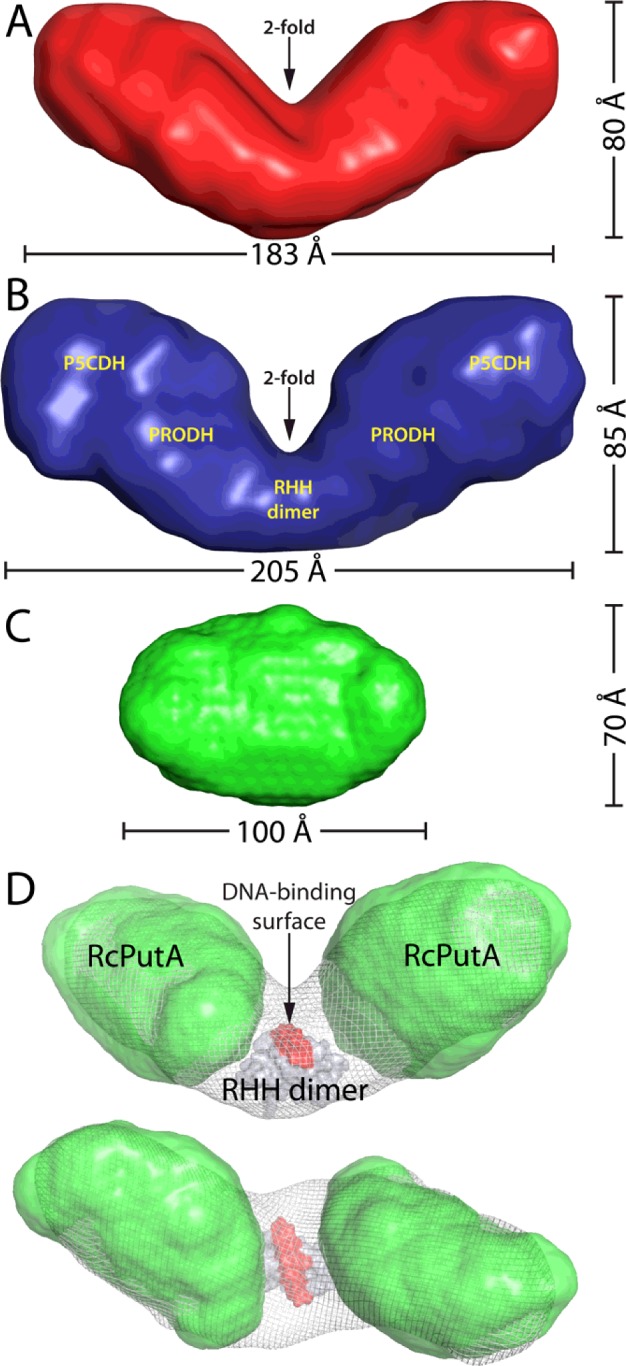
(A) The envelope of EcRHH–RcPutA calculated from 32 independent GASBOR shape reconstruction calculations performed with the assumption of 2-fold symmetry. The normalized spatial discrepancy of the ensemble is 1.7±0.2. (B) The SAXS envelope of EcPutA. Reproduced from [46]: Singh, R.K., Larson, J.D., Zhu, W., Rambo, R.P., Hura, G.L., Becker, D.F. and Tanner, J.J. (2011) Small-angle X-ray scattering studies of the oligomeric state and quaternary structure of the trifunctional proline utilization A (PutA) flavoprotein from Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Chem. 286, 43144–43153. (C) The SAXS envelope of RcPutA. Reproduced from [29]: Luo, M., Christgen, S., Sanyal, N., Arentson, B.W., Becker, D.F. and Tanner, J.J. (2014) Evidence that the C-terminal domain of a Type B PutA protein contributes to aldehyde dehydrogenase activity and substrate channeling. Biochemistry 53, 5661–5673. (D) Orthogonal views of a model of the EcRHH–RcPutA dimer. The shape reconstructions of EcRHH–RcPutA and RcPutA are shown as white mesh and green surfaces respectively. The EcPutA RHH dimer (PDB code: 2GPE) is shown as a grey surface with the DNA-binding surface highlighted in red. This model was created by first fitting the RcPutA envelopes into the shape reconstruction of EcRHH–RcPutA using the Fit-in-Map option of chimaera [53]. Then, the EcPutA RHH dimer was manually docked into the remaining open space so that the molecular 2-fold axis of the RHH dimer is parallel to the 2-fold axis of the EcRHH–RcPutA envelope. This model is consistent with previous SAXS modelling studies of EcPutA [46].
