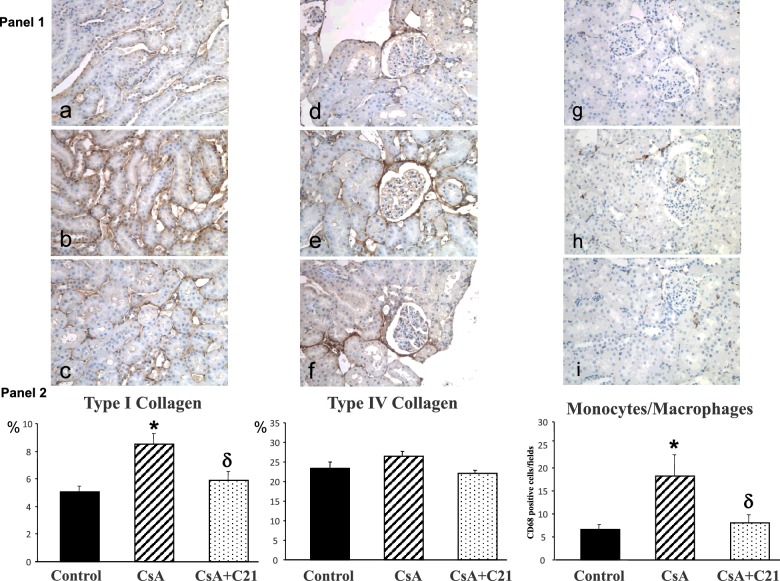
Figure 6. Effects of C21 administration for 28 days on type I and type IV collagen and inflammatory cell infiltration in the kidney of CsA-treated rats.
Panel 1: Representative photomicrographs of immunohistochemical characterization of renal type I and type IV collagen and inflammatory cell infiltration in control (a, d, g), CsA-treated rats (b, e, h), and CsA+C21-treated rats (c, f, i). The immunostaining (brown reaction, 20×) showed a significant increase in interstitial type I collagen in CsA-treated rats (b) compared with control rats (a). C21 administration reduced the increase of type I collagen in CsA-treated rats (c). Type IV collagen in glomerular area did not modify in CsA (e) and CsA+C21-treated (f) rats respect to control rats (d). CsA treatment caused an increase in monocyte/macrophage cell infiltration in CsA-treated rats (h) as compared with control rats (g). C21 administration reduced the increase of monocyte/macrophage cell infiltration in CsA-treated rats (i). Panel 2: Quantification of staining of renal type I collagen, type IV collagen and monocyte/macrophage inflammatory cells in the different groups of rats. Data are means ± S.E.M. *P<0.01 compared with control rats, δP<0.01 compared with CsA-treated rats.