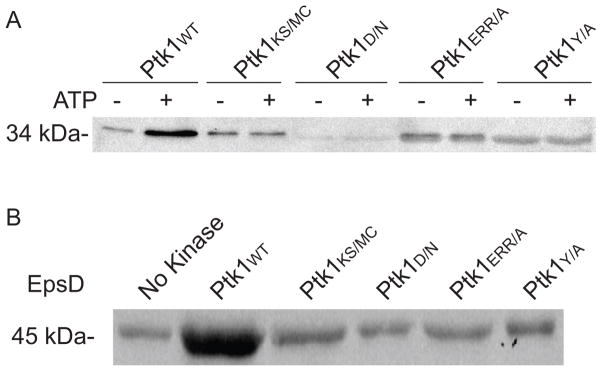
Figure 2.
Auto (A) and substrate (B) phosphorylation by Ptk1 and its phosphotransfer domain mutants. For autophosphorylation, recombinant FPtk1 (Ptk1:541–821) or FPtk1 with mutations in the Walker A (KS/MC), Walker B (D/N), RK (ERR/A) and YC (YA) domains were dephosphorylated with alkaline phosphatase and incubated with or without ATP in the presence of a phosphatase inhibitor. For substrate phosphorylation, Fptk1 and mutant derivatives were incubated with recombinant EpsD (PGN_0224) in the presence of ATP and a phosphatase inhibitor. The phosphorylation level of proteins was determined by Western blotting with phosphotyrosine antibodies.