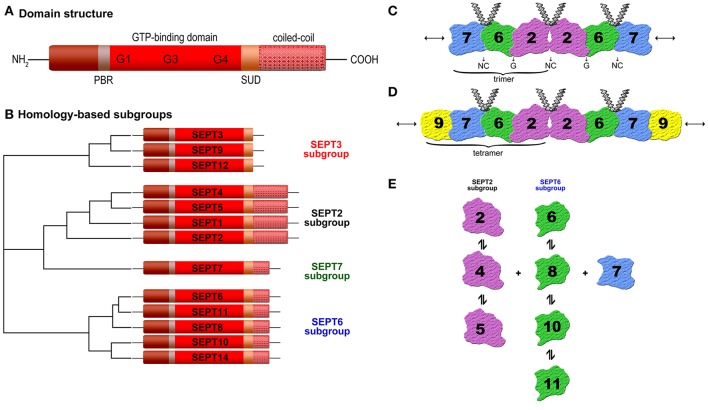
Figure 1.
(A) Schematic septin domain structure. Septins share a conserved GTP-binding domain, a phosphoinosite-binding polybasic region (PBR), a septin unique domain (SUD), and most of them one or more coiled-coil domains. The length and amino acid sequence of the N- and C-terminus vary (according to Trimble, 1999). (B) Homology-based subgroups. The 13 human septins (SEPT1 to SEPT12 and SEPT14) are classified into four subgroups (SEPT3, SEPT2, SEPT7, and SEPT6) based on sequence homology and coiled-coil domains (Macara et al., 2002; Kinoshita, 2003b). (C) Structure of the SEPT2-6-7 complex. Two copies of each septin are symmetrically arranged (SEPT7-6-2-2-6-7) to generate a hexamer by alternating N- and C-termini (NC) and G-interface (GTP-binding domain) (Sirajuddin et al., 2007). (D) Structure of the SEPT2-6-7-9 complex (Sandrock et al., 2011; Kim et al., 2011). (E) Binding preferences of individual septins to other septins (Sandrock et al., 2011).