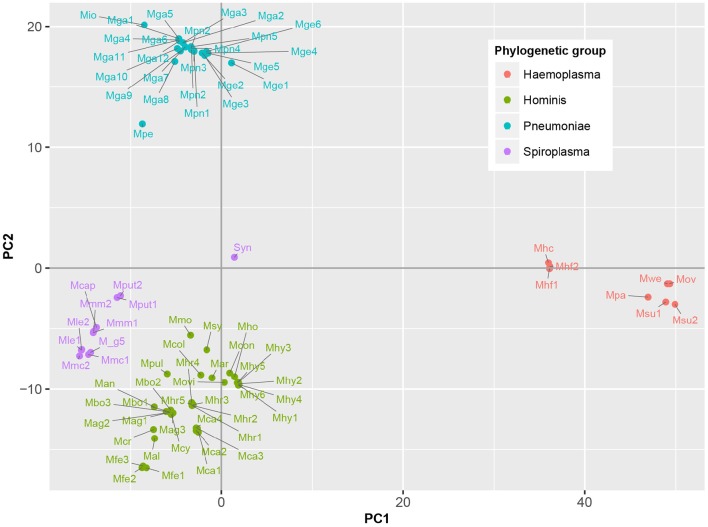
Figure 4.
Functional differentiation of mycoplasma species. Score plot is shown of principal component analysis done on the presence/absence matrix of the 80 mycoplasma strains and the synthetic bacterium JCVI-Syn3.0. Main phylogenetic groups are color coded. Note the separation of mycoplasma species infecting blood and tissue. Mag, M. agalactiae; Mal, M. alligatoris; Man, M. anatis; Mca, M. canis; Mcol, M. columbinum; M_g5, M. g5847, Mge, M. genitalium; Mio, M. iowae; Mmc, M. mycoides capri; Movi, M. ovipneumoniae; Mpn, M. pneumoniae; Mar, M. arthritidis; Mbo, M. bovis; Mca, M. capricolum subsp. capricolum; Mcon, M. conjunctivae; Mcr, M. crocodyli; Mcy, M. cynos; Mfe, M. fermentans; Mga, M. gallisepticum; Mhc, M. haemocanis; Mhf, M. haemofelis; Mho, M. hominis; Mhy, M. hyopneumoniae; Mhr, M. hyorhinis; Mle, M. leachii; Mmo, M. mobile; Mmm, M. mycoides subsp. mycoides; Mov, M. ovis; Mpa, M. parvum; Mpe, M. penetrans; Mpul, M. pulmonis; Mput, M. putrefaciens; Msu, M. suis; Msy, M. synoviae; Mwe, M. wenyonii; Syn, JCVI-Syn3.0. Numbers relate to strains (Table S4).