Figure 2.
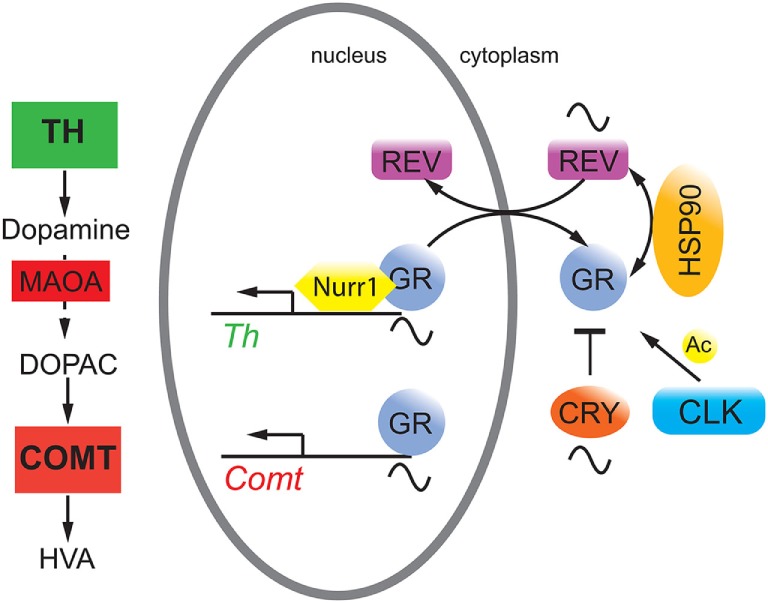
Hypothetical model on the interaction of circadian clock proteins with the glucocorticoid receptor (GR). REV-ERBα (REV, purple) gates nuclear localization of the GR (gray) via an unknown mechanism probably involving heat shock protein 90 (HSP90, yellow). GR function is inhibited by cryptochrome (CRY, orange) proteins and is modulated by CLOCK (blue) via acetylation (Ac), although it is unclear whether this happens in the cytoplasm and/or the nucleus. GR regulates target genes such as catechol-O-methyltransferase (Comt) whose protein is an enzyme (COMT, red square) that degrades 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid (DOPAC) to homovanillic acid (HVA). GR may also interact with Nurr1 to modulate tyrosine hydroxylase (Th) expression thereby influencing dopamine production.
