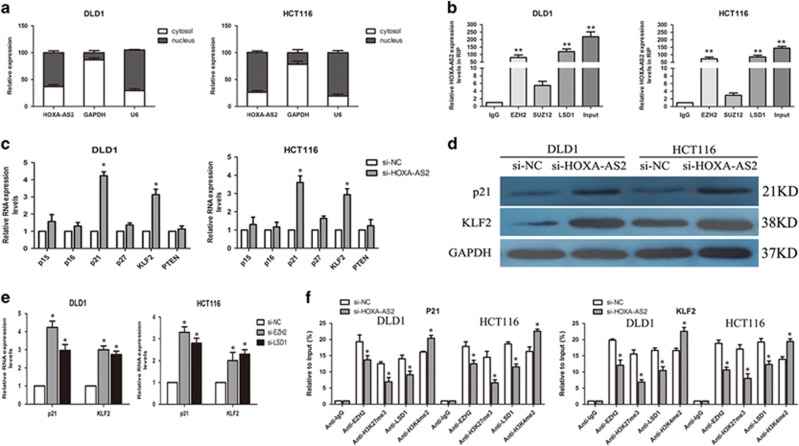
Figure 4.
HOXA-AS2 epigenetically silences p21 and KLF2 transcription by binding to EZH2 and LSD1. (a) qRT–PCR analysis of HOXA-AS2 nuclear and cytoplasmic expression levels in DLD1 and HCT116 cells. U6 was used as a nucleus marker, and GAPDH was used as a cytosol marker. (b) RIP experiments were performed in DLD1 and HCT116 cells, and the coprecipitated RNA was subjected to qRT–PCR for HOXA-AS2. The fold enrichment of HOXA-AS2 in EZH2/SUZ12/LSD1 RIP is relative to its matched IgG control. (c) The levels of p15, p16, p21, p27, KLF2 and PTEN mRNA were determined by qRT–PCR when knockdown of HOXA-AS2. (d) The p21 and KLF2 protein levels were determined by western blot in HOXA-AS2 knockdown in DLD1 and HCT116 cells. (e) The p21 and KLF2 expression levels were determined by qRT–PCR when knockdown of EZH2 or LSD1 in DLD1 and HCT116 cells. (f) ChIP-qRT–PCR of EZH2/LSD1 occupancy and H3K27me3/H3K4me2 binding in the p21 and KLF2 promoters in DLD1 and HCT116 cells treated with si-HOXA-AS2 (48 h) or si-NC; IgG as a negative control. Error bars indicate mean±s.e.m. *P<0.05, **P<0.01. ChIP, chromatin immunoprecipitation; NC, negative control.