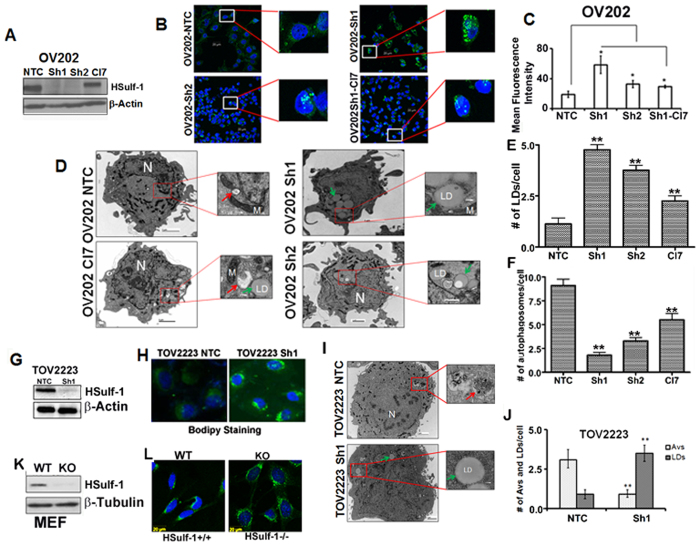
Figure 1. HSulf-1 loss promotes lipid droplet biogenesis and defective autophagy in OV202, TOV2223 and HSulf-1 knockout mouse embryonic fibroblast cells.
(A) Protein expression of HSulf-1 was assessed by western blot in OV202 clones (NTC, Sh1, Sh2 and Cl7 cells). β-Actin was probed as a loading control. (B) OV202NTC, Sh1, Sh2 and Cl7 cells were labeled with Bodipy 493/503 (green) and DAPI (Blue) to determine the cytoplasmic lipid droplets (LD) and nuclei respectively. (C) Mean fluorescence of Bodipy in NTC, Sh1, Sh2 and Cl7 is measured using Carl Zeiss Zen (2009) software and the data is plotted as a bar diagram. Sh1 and Sh2 cells were compared to NTC cells whereas Cl7 cells were compared to Sh1 cells. In both the cases, (p ≤ 0.05) (D) Representative trans-electron microscopic (TEM) images of NTC, Sh1, Sh2 and Cl7 cells are shown; cytoplasmic LDs are marked with green arrows, whereas red arrows indicate autophagic vesicles (AV). (E and F) LDs and AVs quantified in NTC, Sh1 and Sh2 cells and plotted in a bar graph. Sh1 and Sh2 cells were compared to NTC cells and, Cl7 cells were compared to Sh1 cells. In all the cases p ≤ .0.01 (G) Protein expression of HSulf-1 in TOV2223 NTC and Sh1 cells is detected by immunoblot analysis; β-actin was probed as a loading control. (H) Bodipy staining performed in TOV2223 NTC and Sh1 cells to detect LDs. (I). Representative TEM images of TOV2223 NTC and Sh1 cells are shown. (J) AVs and LDs in TOV2223 cells are quantified. We compared TOV2223 NTC cells to TOV2223 HSulf-1 knockdown Sh cells and found significant differences in the # of AVs and LDs (K) Protein expression of HSulf-1 in Mouse Embryonic Fibroblast (MEF) wild type (WT) and HSulf-1 knock out (Sulf-1−/−) cells is detected by western blotting. β-Tubulin was used as a loading control. (L) MEF cells were labeled with Bodipy 493/503 (green) to determine cytoplasmic LDs. Data are shown as mean ± SD of 3 replicates per treatment. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01.