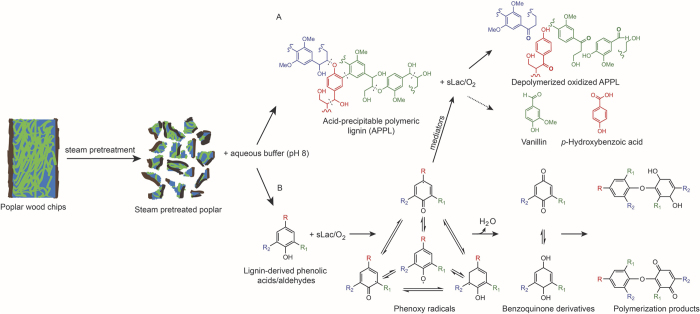
Figure 7. A proposed mechanism for the sLac-catalyzed delignification of SPP.
Representations of poplar wood chips and the steam-pretreated fragments show cellulose (blue), hemicelluloses (green) and lignin (brown). Path A shows the release of APPL from SPP followed by depolymerization, benzylic oxidation (bold), and the production of monoaryls due to the direct interaction of sLac with lignin. Path B shows the sLac-mediated oxidation of monoaryls released into the aqueous phase during the incubation of SPP. The generated phenoxy radicals can either act as mediators to initiate radical depolymerization of the lignin or initiate polymerization reactions. For protocatechuic acid R=COOH, R1=OH and R2=H; for syringic acid R=COOH, R1=OCH3 and R2=OCH3; for syringaldehyde R=CHO, R1=OCH3 and R2=OCH3; for vanillic acid R=COOH, R1=OCH3 and R2=H.