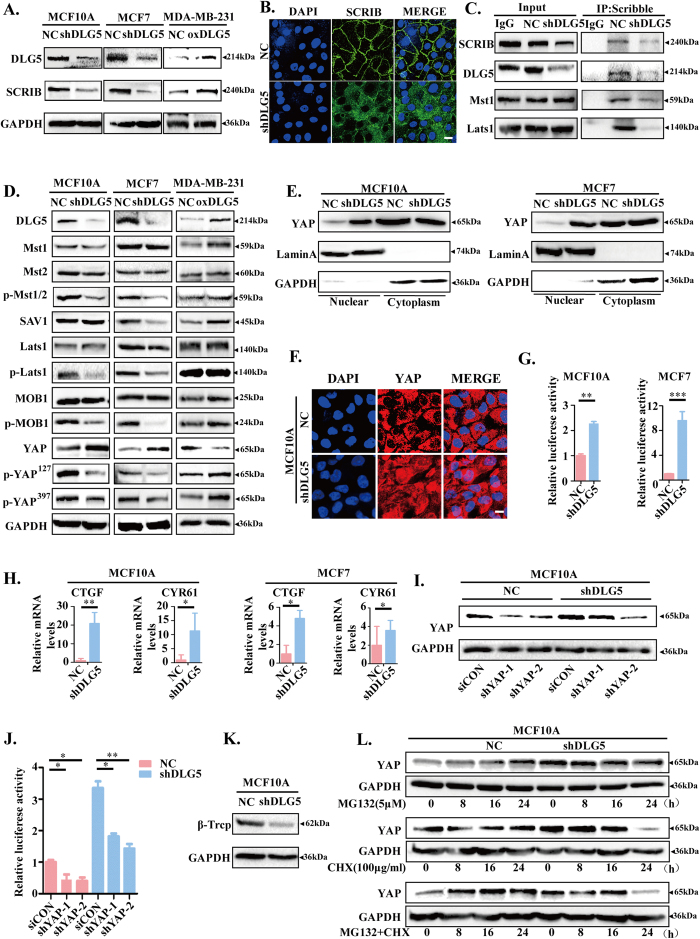
Figure 5. Loss of DLG5 inhibits the Hippo signaling pathway.
(A) Western blot analysis of SCRIB in NC, MCF10A-shDLG5, MCF7-shDLG5 and MDA-MB-231-oxDLG5 cells. (B) Immunofluorescence analysis of SCRIB localization in NC and MCF10A-shDLG5 cells. Scale bar, 25 μm. (C) Co-IP assay and western blot analysis of the interaction of DLG5, MST1, and Lats1 with SCRIB in NC and MCF10A-shDLG5 cells. (D) Western blot analysis of Hippo signaling pathway components in NC, MCF10A-shDLG5, MCF7-shDLG5, and MDA-MB-231-oxDLG5 cells. (E,F) Western blot analysis and immunofluorescence analysis of the nuclear and cytoplasmic distribution of YAP in NC and MCF10A-shDLG5 cells. Scale bar, 25 μm. (G) TEAD activity was analyzed by luciferase assay. (H) The relative mRNA levels of CTGF and CYR61 were analyzed by RT-PCR. I. Western blot analysis of YAP expression following siRNA-mediated YAP knockdown. (J) TEAD activity was analyzed by luciferase assay following siRNA-mediated YAP knockdown. (K) Western blot analysis of β-Trcp expression in NC and MCF10A-shDLG5 cells. (L) NC and MCF10A-shDLG5 cells were treated with MG132 (5 μM) and/or CHX (100 μg/ml) for 8, 16, and 24 hrs. Extracts were analyzed by western blot.