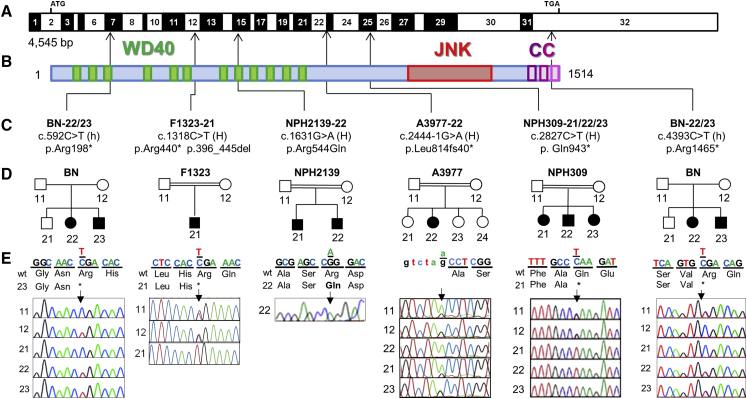
Figure 1.
Biallelic Mutations in MAPKBP1 Cause Nephronophthisis
(A) Exon structure of MAPKBP1 cDNA. Positions of start codon (ATG) and stop codon (TGA) are indicated.
(B) Domain structure of the protein. MAPKBP1 contains 12 WD repeats (green), located at the N terminus, a JNK-binding region located in the C-terminal part (red), and conserved coiled-coil domains at the C terminus (CC, purple).
(C) Relation of four homozygous (H) and two compound heterozygous mutations (h) to exons and protein domains is indicated by black arrows.
(D and E) Pedigrees (D) and chromatograms and segregation (E). Mutated nucleotides are shown above wild-type. In addition, individuals BN-21 and BN-23 also presented with retinitis pigmentosa (RP) linked to a homozygous mutation in PDE6A.
See Figure S5. Segregation of the MAPKBP1 mutations was not examined in family NPH2139 due to the unavailability of the DNA of the affected brother and the parents.