Fig. 8.
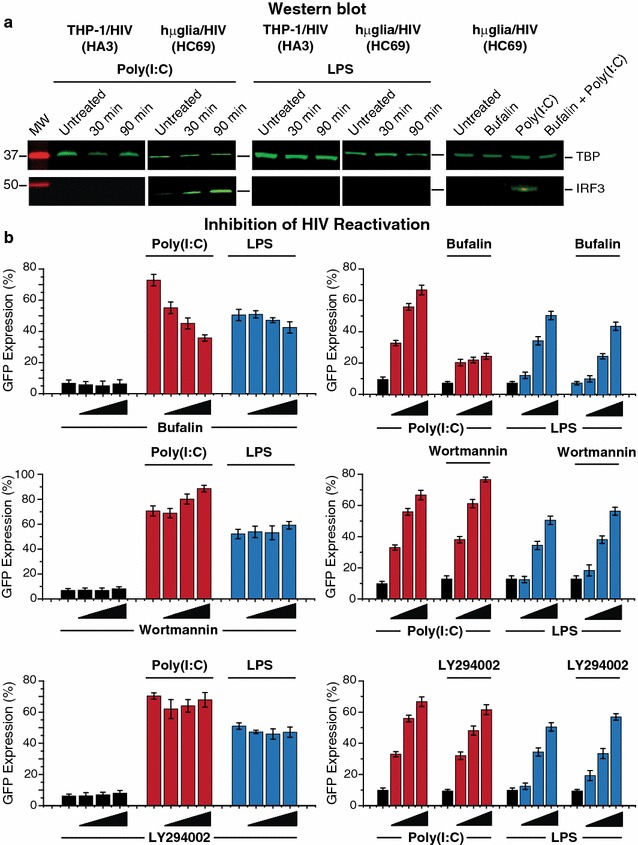
Poly (I:C)-mediated HIV reactivation in hµglia/HIV (HC69) cells requires IRF3 nuclear recruitment. a Representative Western blot analysis images of IRF3 nuclear recruitment after poly (I:C) stimulation. Cells were untreated or treated with poly (I:C) (1 µg/mL), or LPS (1 µg/mL), as negative control, for 30 or 90 min prior to nuclear extracts purification. Far right Representative Western blot analysis images of IRF3 nuclear recruitment after poly (I:C) stimulation in the absence or presence of bufalin. Cells were untreated or treated with poly (I:C) (1 µg/mL), bufalin (25 nM), or a combination of both for 90 min prior to nuclear extracts purification. For all blots, anti-TBP antibody was used as loading control. Molecular weights of IRF3 and TBP are indicated at left. b Pharmacological inhibition of poly (I:C)-mediated HIV reactivation. Left hµglia/HIV (HC69) cells were untreated or pre-treated with either poly (I:C) (1 µg/mL) or LPS (500 pg/mL) for 30 min prior to addition of inhibitors [bufalin (0, 5, 10, and 25 nM); wortmannin (0, 0.5, 2, and 5 nM); LY294002 (0, 0.5, 2, and 5 µM)]. Right hµglia/HIV (HC69) cells were untreated or pre-treated with inhibitors [bufalin (25 nM); wortmannin (5 µM); LY294002 (5 µM)] for 30 min prior to no-addition or addition of either poly (I:C) (0, 0.1, 0.5, and 1 µg/mL) or LPS (0, 20, 100, and 500 pg/mL), as indicated
