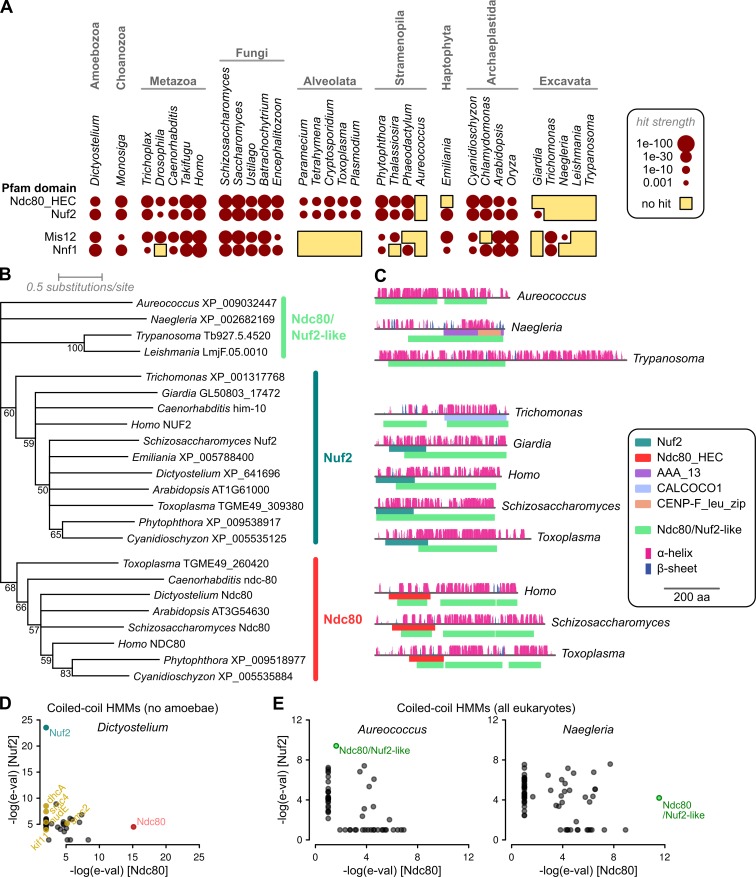
Figure 1.
Identification of Ndc80- and Nuf2-like sequences across eukaryotes. (A) Most excavates and the golden alga A. anophagefferens lack proteins matching either Ndc80_HEC or Nuf2 Pfam domains (e-value ≤ 0.001). A similar, but not identical, distribution exists for Mis12 and Nnf1 domains, with notable additional absence in Alveolata. (B) Maximum likelihood phylogeny of Ndc80/Nuf2-like protein sequences. Tree represents a majority consensus from 500 bootstrapped inferences based on 406 aligned residues. Numbers show bootstrap support for nodes. (C) Predicted protein architectures (secondary structure features and Pfam domains) of example sequences, showing also position of hits to a pan-Ndc80/Nuf2 HMM. (D) The coiled-coil tails of both Ndc80 and Nuf2 contain information specific to these families; HMMs built only from regions of Ndc80 or Nuf2 homologues outside of the CH fold, and excluding all sequences from Amboebae, specifically identify Ndc80 and Nuf2 from the predicted proteome of Dictyostelium discoideum. (E) Similar models including all eukaryotes specifically identify the Ndc80/Nuf2-like sequences detected by the pan-Ndc80/Nuf2 HMM.