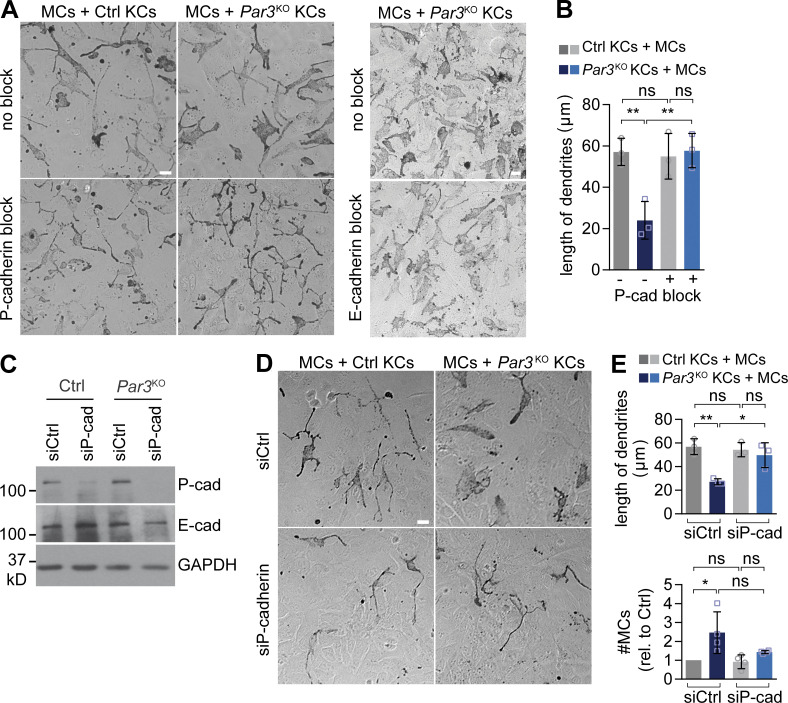
Figure 5.
P-cadherin is required for MC dedifferentiation and hyperplasia upon loss of epidermal Par3. (A) Antibody-mediated P-cadherin block (left) but not E-cadherin block (right) in direct co-culture restores MC dendricity in MCs co-cultured with Par3KO KCs. Bars, 20 µm. Data are representative of three independent experiments. (B) Quantification of A (>10 images per condition). Data are pooled and represented as mean ± SD. n = 3 biological replicates per group. **, P = 0.0079 and 0.0071; ns, P = 0.9691 and 0.8514; one-way ANOVA with Tukey posthoc test. (C) Western blot analysis for P- and E-cadherin expression in control and Par3KO KCs after siRNA transfection, confirming efficient P-cadherin knockdown. Data are representative of three independent experiments. (D) siRNA-based P-cadherin knockdown (bottom) restores shape and dendritic length of MCs in direct co-culture with Par3KO KCs. Bar, 20 µm. Data are representative of four independent experiments. (E) Quantification of D (>15 images per condition). Data are pooled and represented as mean ± SD. Dendritic length: n = 3 biological replicates per group; *, P = 0.0184; **, P = 0.0038; one-way ANOVA with Tukey posthoc test. MC number: n = 4 biological replicates per group; *, P = 0.0179; ns, P = 0.617; one-way ANOVA with Tukey posthoc test. cad, cadherin; Ctrl, control; rel., relative.