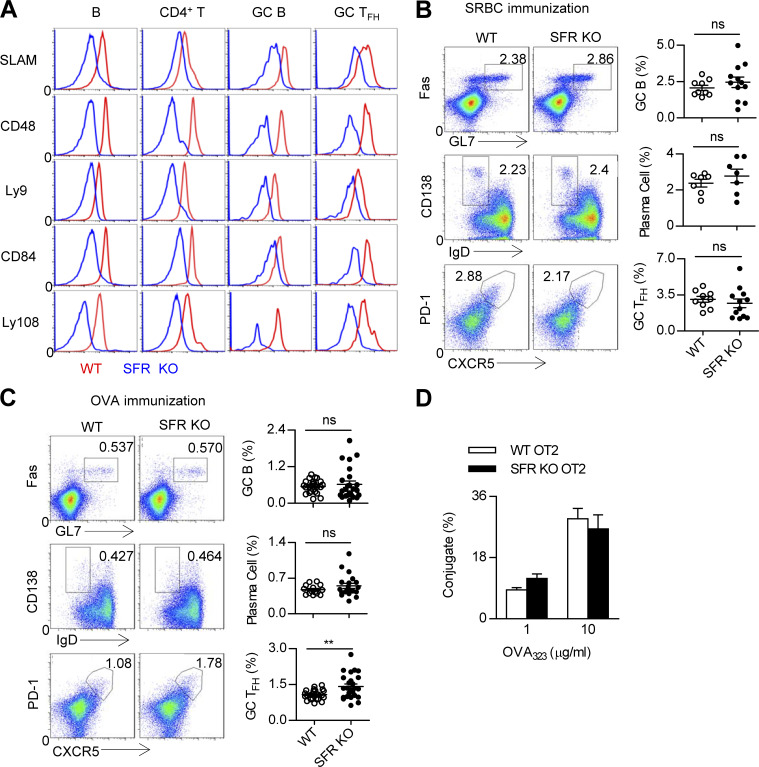
Figure 7.
SFR deficiency does not affect humoral immunity. (A) Flow cytometry analysis of SFR expression in resting splenic B cells (CD19+) and CD4 T cells (CD4+CD19−) from nonimmunized WT mice as well as GC B cells (CD19+GL7hiFashi) and GC TFH cells (CD4+CD19−CXCR5hiPD1hi) from SRBC-immunized WT mice. Respective SFR-deficient cells were used as negative controls. The data are representative of three experiments. (B and C) Representative flow cytometry plots (left) and percentages (right) of splenic GC B cells (CD19+FashiGL7hi), plasma cells (CD19+IgDloCD138hi), and GC TFH cells (CD4+CD19−PD1hiCXCR5hi) from WT and SFR KO mice 7 d after SRBC immunization (B) or 9 d after OVA immunization (C). Data represent the mean ± SEM of 9–25 mice per group. **, P < 0.01. (D) Percentage of T–B conjugation (number of CD4+CD19+ cells out of total number of CD4+ cells). OT-II CD4+ T cells from WT and SFR-deficient mice and B cells were pulsed with OVA323–339 peptide at the indicated concentrations. The data are representative of three experiments and show the mean ± SEM of three mice per group.