Fig. 1.
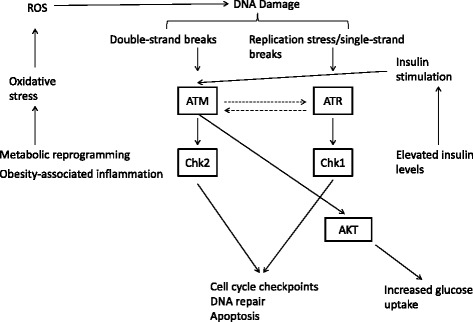
Schematic representation of the relationship between obesity-related alterations and the DDR machinery. The increased production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), stemming from both metabolic reprogramming of cancer cells and the obesity-related inflammatory status (left), results in elevated levels of DNA damage (oxidative stress-related DNA damage) with the consequent activation of the ATM and ATR pathways. Moreover, insulin, whose levels increase in obese patients (insulin resistance), activates ATM that in turn increases glucose uptake via AKT (right)
