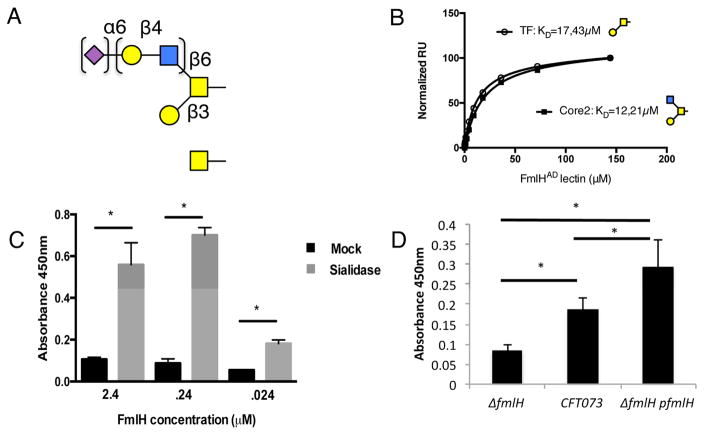
Figure 2. FmlHAD binding to O-glycans.
(A) Schematic representation of top-scoring glycan profiles for FmlHAD. Gal, GalNAc, GlcNAc and Neu5Ac are shown as yellow circle and yellow, blue or magenta square, respectively. (B) SPR saturation binding experiments of FmlHAD interacting with immobilized Thomsen-Friedenreich (TF) and Core2 carbohydrates, revealing dissociation constants (KD) of 17.43 μM and 12.21 μM, respectively. (C) ELISA showing FmlHAD binding to BSM with and without sialidase pretreatment, n=4. (D) ELISA results examining CFT073, CFT073ΔfmlH, or CFT073ΔfmlH:fmlH binding to sialidase treated BSM coated plates, n=4. Columns represent the mean of each data set and error bars display the standard deviation. Asterisks denote (C) p<0.0005 (D) p<0.05, Student’s t test.