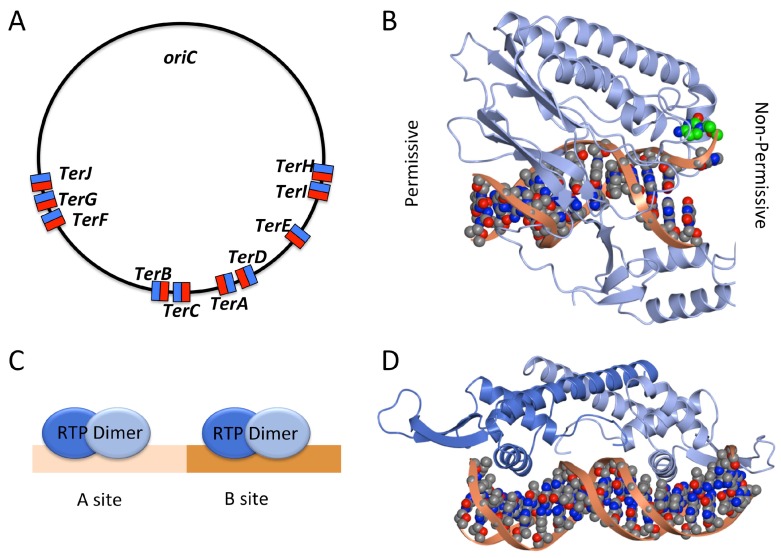
Figure 3.
(A) Location and orientation of Ter sites in E. coli: permissive face shown in blue, non-permissive face shown in red; (B) Structure of the Tus-Ter complex (PDB code: 2EWJ) showing the permissive face (left) and the non-permissive face (right). On the non-permissive face a specific cytosine base (green) flips into Tus when double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) is unwound by the oncoming replication fork, creating a ‘locked’ complex; (C) Schematic image of two RTP dimers binding at the A and B sites of the Bacillus terminus region; (D) Structure of an RTP dimer bound to dsDNA (PDB code: 2EFW) with the sequence of a B-site region; one molecule displays a ‘wing up’ conformation (adjacent to the A site) and the other a ‘wing down’ conformation. (B), (D) and subsequent structural figures were rendered in CCP4MG [34].