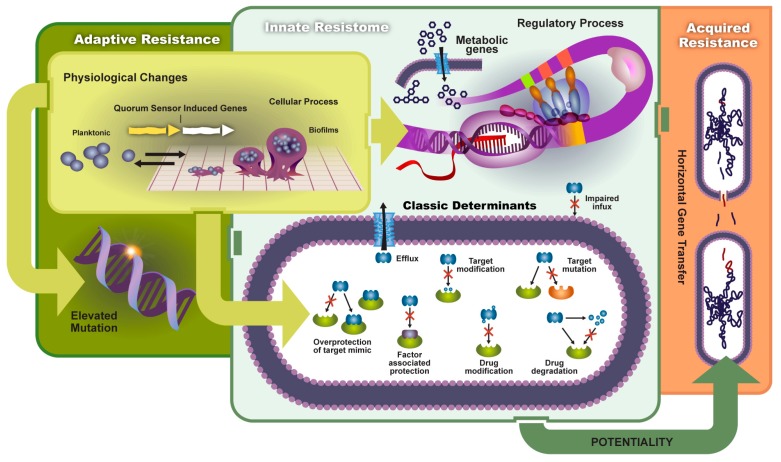
Figure 1.
The transmission and mechanisms of antibiotic resistance and virulence can be divided into adaptive resistance, innate resistance, and acquired resistance. Environmental factors can prompt physiological changes and lead to: (1) elevated mutation rates; (2) changes in metabolic genes and regulatory processes; and (3) a host of classic antibiotic inactivation and resistance mechanisms (classic determinants). Such resistance and increased virulence can potentially be shared among bacteria leading to acquired resistance.