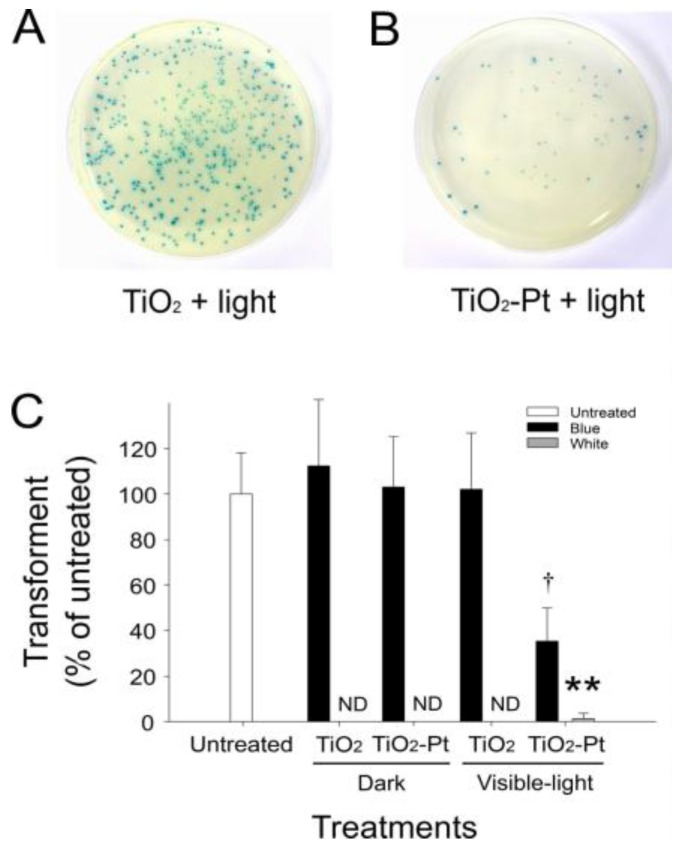
Figure 4.
Detection of mutated clones using lacZ α-peptide complementation. (A,B) After being complemented with lacZ α-peptide expression, the transformants are displayed as blue colonies on the agar plates with 5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl-β-d-galactopyranoside. The VLRP TiO2-Pt NP-mediated photocatalysis markedly reduces the number of transformants, compared with the control groups using UV-responsive TiO2 NPs, under visible light illumination. (C) Quantified results show that TiO2-Pt photocatalysis can induce the formation of white colonies. This indicates that mutations hit the lacZα region because of a loss-of-function (loss-of-complementation) phenotype, compared with the wild-type plasmid-transformed blue colonies. ND: no detected colony. * p < 0.05 vs. both blue groups of TiO2-visible light and TiO2-Pt-dark; ** p < 0.01 vs. respective blue groups. n = 6, three experiments with two replicates.