Figure 2. Accuracy of multi-marker models in the diagnosis of TB disease.
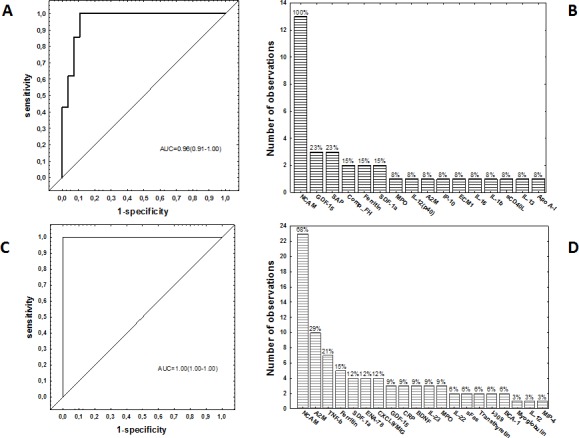
Receiver operator characteristics (ROC) curve showing the accuracy of the most accurate six-marker biosignature (NCAM, SAP, IL-1β, sCD40L, IL-13 and Apo A-1) in the diagnosis of TB disease in all study participants, regardless of HIV infection status A., frequency of analytes in the top 13 general discriminant analysis (GDA) models that most accurately classified study participants as TB disease or ORD irrespective of HIV status B., ROC curve showing the accuracy of the most accurate six-marker biosignature (NCAM+A2M+IL-22+ferritin+ myoglobulin+IL-12(p40) or NCAM+A2M+IL-22+ferritin+TNF-β+MIP-4) in the diagnosis of TB disease in HIV negative study participants C., and frequency of analytes in the top 34 GDA models that most accurately classified study participants as TB disease or ORD in the absence of HIV infection D.. The bar graphs B. and D. indicate the frequency of analytes in the most accurate GDA models.
