Figure 8. Lung tumor inhibitory effects of intranasally administered liposomal honokiol in A/J mice.
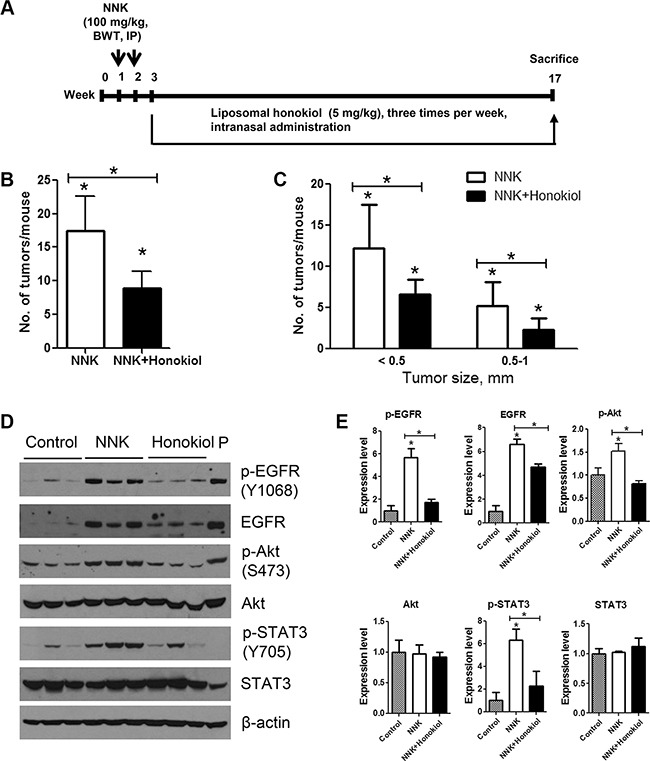
(A) Experimental design of the study. Three groups of female A/J mice (n = 15/group) were established. Two groups (NNK control and NNK + honokiol groups) received two doses of NNK (100 mg/kg body weight, ip injection) whereas the vehicle group was injected with physiological saline solution. Beginning 1 week after the final NNK dose, mice in the NNK + honokiol group received liposomal honokiol (5 mg/kg) by intranasal instillation three times a week. Mice in the NNK control group received empty liposome three times a week. The study was terminated at week 17. Upon termination of the study, lungs were harvested, tumors on the surface of the lung were counted (B) and the size of the tumors determined (C) under stereo microscope. (D) Representative western immunoblots showing the effects of honokiol on the expression of EGFR and its downstream effectors. Normal lung tissues (vehicle control group) or lung tumor tissues (from NNK control and NNK + honokiol groups) were randomly selected (three mice/group), tissue lysates prepared and individually analyzed by Western immunoblotting as described in the Materials and Methods section. Immunoblotting studies were repeated three times with different samples. Cell lysates from lung adenocarcinoma A549 cell line were used as positive control and loaded on to the last lane (P). (E) Quantification of the western blot results. Densitometry measurements of western blot bands were performed using digitalized scientific software program UN-SCAN-IT software. *P < 0.05, Control group versus NNK group and NNK group versus NNK + honokiol group.
