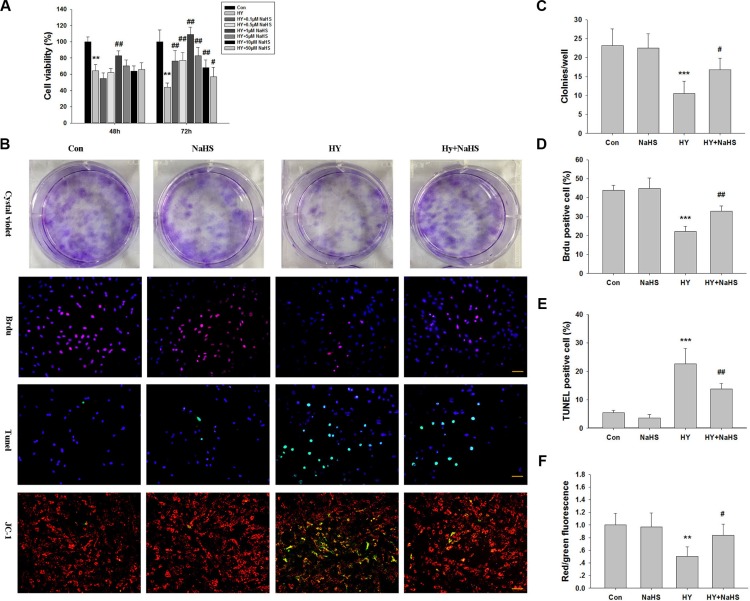
Figure 1. Effects of NaHS treatment on cell viability in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) in vitro.
(A) BMSCs maintained in 1% serum medium exposed to hypoxia (hypoxia-ischemic injury) were incubated in the absence or presence of indicated concentrations of NaHS (0.1–50 μM) for 48 h and 72 h and cell viability was examined by MTT assay. Values of cell viability were expressed as a percentage relative to those obtained in controls. Values represent the mean ± SD of n = 6. (B) BMSCs exposed to hypoxia-ischemic were incubated in the absence or presence of indicated concentrations of NaHS (1 μM) for 72 h. The cells were then subjected to crystal violet assay, BrdU assay (red), tunnel staining, and JC-1 staining, counterstained with DAPI (blue). Scale bar = 50 μm. (C) The graphs indicate the number of positive colonies/well by crystal violet staining, n = 6. (D) Quantification of BrdU positive BMSCs over the total DAPI-positive cells, n = 4. (E) Quantification of Tunnel positive BMSCs over the total DAPI-positive cells. Values represent the mean ± SD of n = 4. (F) Quantitative analysis of the ratio of red/green fluorescence, n = 6. Values represent the mean ± SD. **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 Hypoxia (Hy) VS Control (Con); #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01 Hy+ NaHS VS Hy.