Figure 5. GHK-Cu attenuated LPS-induced acute pulmonary inflammation in mice.
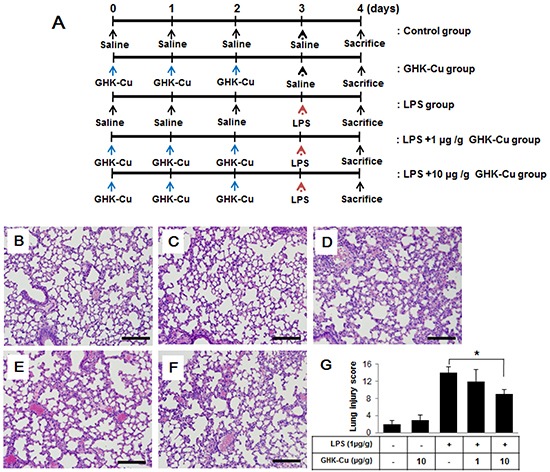
Mice were injected i.p. with 1 or 10 μg/g GHK-Cu every 24 h for 3 days in 100 μl of saline, while control mice were injected i.p. with 100 μl of saline. Intratracheal LPS at 1 μg/g dissolved in 50 μl of saline or saline alone was administered 24 h after the third injection of GHK-Cu or saline. At 24 h after LPS administration, the mice were sacrificed and their left lungs were fixed. Then, tissue sections were stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H & E). A. Experimental scheme for LPS treatment with or without GHK-Cu. (n = 7 mice per group). B. CTL; C.10 μg/g GHK-Cu; D. LPS; E. LPS + 1 μg/g GHK-Cu; F. LPS + 10 μg/g GHK-Cu. G. Lung injury scores were calculated according to the sum of the levels of cell infiltration and damage levels as assessed from the lung sections. The data represent the means ± SD (n =7 per group). *p < 0.05, statistically significant difference. Scale bars represent 100 μm. CTL, control.
