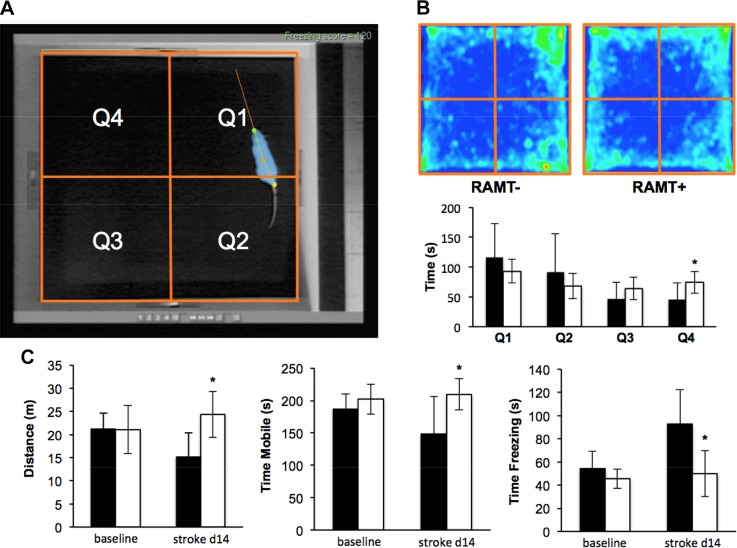
Figure 4.
RAMT improves poststroke sensorimotor function. A) Representative screen capture of baseline RAMT− (control) rat with software overlay tracking head (green dot), middle body (orange dot), tail (yellow dot), and motion vector (orange line) in real time. Software was used to divide the open field into 4 quadrants (orange boxes Q1–Q4) for tracking the amount of time spent in each zone during the test. B) Average heat map of RAMT− and RAMT+ rats during field test on poststroke d 14. A video tracking system calculated mean time spent in each zone (RAMT−, black bars; RAMT+, white bars). C) Compared to RAMT− rats, RAMT+ rats traveled greater distance and spent more time mobile and less time freezing on poststroke d 14. Data are means ± sd (n = 7). *P < 0.05 vs. RAMT− at same timepoint.