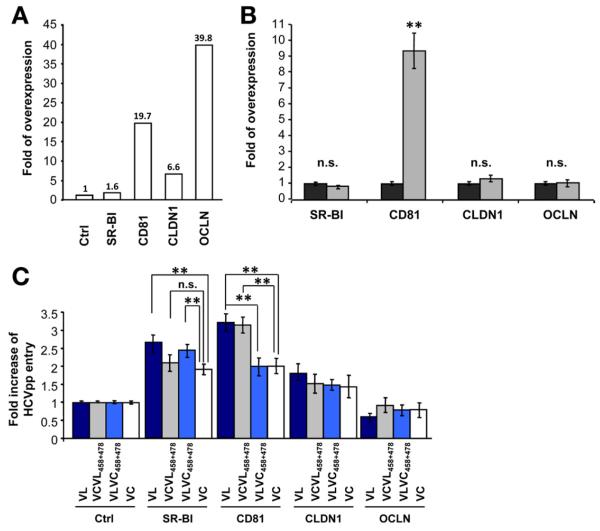
Figure 2.
Altered use of CD81 is responsible for enhanced viral entry of the escape variant. (A) Entry factor expression in clones of SR-BI-, CD81-, CLDN1-, or OCLN-transduced Huh7.5.1 cells. The relative overexpression of each entry factor was determined by flow cytometry and is indicated as fold expression compared with parental Huh7.5.1 cells. (B) Entry factor expression in pools of CD81-overex-pressing Huh7.5.1 cells (grey bars). The relative entry factor expression was determined as described in panel A. (C) Receptor dependency of patient-derived HCVpp entry. Parental and transduced Huh7.5.1 cells were incubated with parental or chimeric HCVpp and viral entry was determined as described in Figure 1. Viral entry is expressed as the fold-change of viral entry compared with parental cells. Means ± standard deviation from 3 independent experiments performed in triplicate are shown. Significant differences in HCVpp entry between variants are indicated (**P < .001).