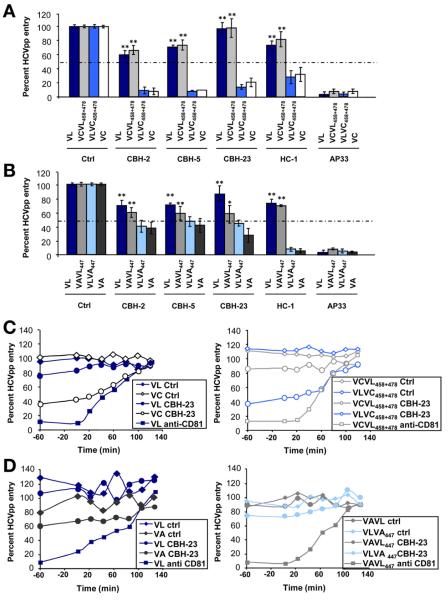
Figure 5.
Mechanisms of viral evasion from neutralizing antibodies. (A and B) Escape from neutralization by HMAbs directed against conformational and linear epitopes. HCVpp produced from isolates shown in Figure 1 were incubated with HMAbs (Supplementary Table 1) or control Ab (10 μg/mL) for 1 hour at 37°C before incubation with Huh7.5.1 cells. Results are expressed as the percentage of viral entry relative to HCVpp incubated with control mAb. Means ± standard deviation from at least 4 experiments performed in triplicate are shown. Significant differences in HCVpp entry between variants are indicated (**P < .001). (C and D) Escape from neutralization of anti-E2 antibody CBH-23 in kinetic assays. Kinetics were performed as described in Figure 3 (HMAb, 10 μg/mL; JS-81, 5 μg/mL). One representative experiment of 4 is shown.