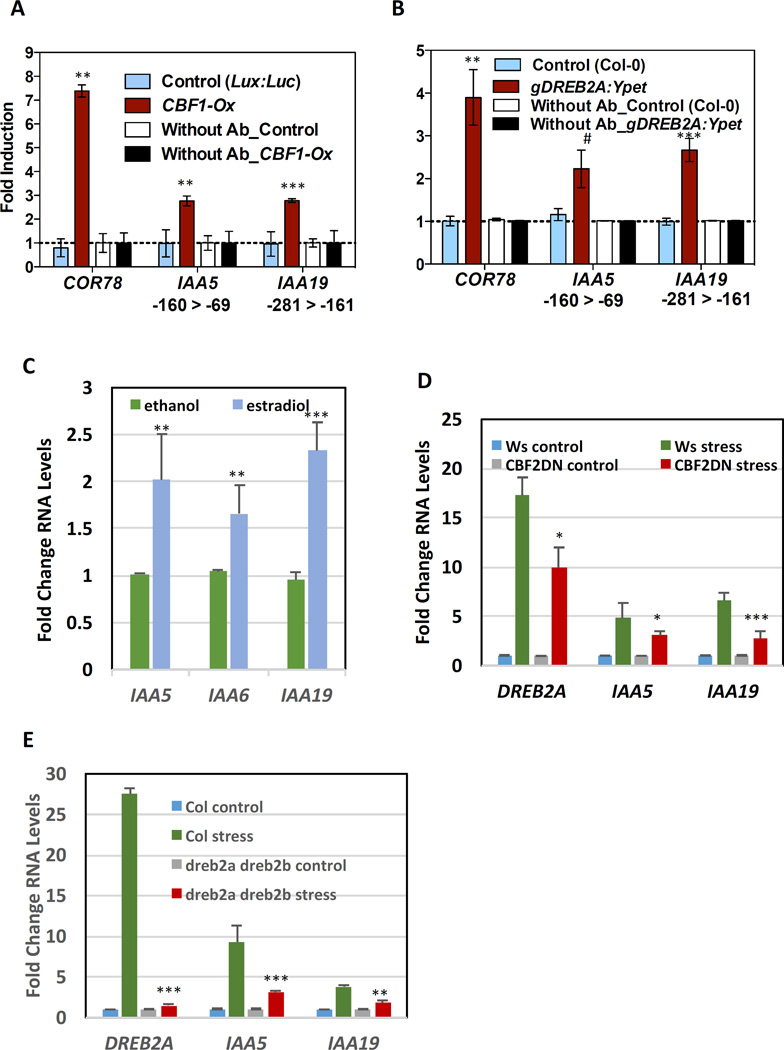
Fig 3. DREB/CBFs regulate transcription of IAA5, IAA6, and IAA19.
(A–B) CBF1 and DREB2A bind to the promoter of COR78, IAA5 and IAA19. (A) CBF1 binds to the promoter of COR78, IAA5 and IAA19 in 10-day-old light-grown whole seedlings. (B) DREB2A binds to the promoter of COR78, IAA5 and IAA19 in the roots of 10-day-old light-grown seedlings that were desiccated for 1h. Sonicated chromatin was immunoprecipitated either with or without anti-GFP antibody. Fold induction was normalized to no antibody and wild-type controls. Data represents mean with standard error from two independent biological replicates with two technical replicates for CBF1 and three independent biological replicates for DREB2A. Differences are significant at p<0.01(**), p<0.005 (***), and p<0.08 (#). (C, D, E) CBF1 and DREB2A directly regulate IAA5 and IAA19 transcription. (C) Estradiol regulated DREB2A overexpression (Est.≫DREB2A) induces IAA5, IAA6 and IAA19 expression. Data represent means with standard error from three independent biological replicates. Significant at p<0.005 (***) and p<0.05 (**). (D) Expression of DREB2A, IAA5 and IAA19 in CBF2DN line after 1 h desiccation. Differences are significant at p<0.05 (*) and p<0.005 (***). (E) IAA5 and IAA19 levels in dreb2a-dreb2b double mutant after 1 h desiccation. Differences are significant at p<0.005 (***) and p<0.01 (**) Student’s t-test.