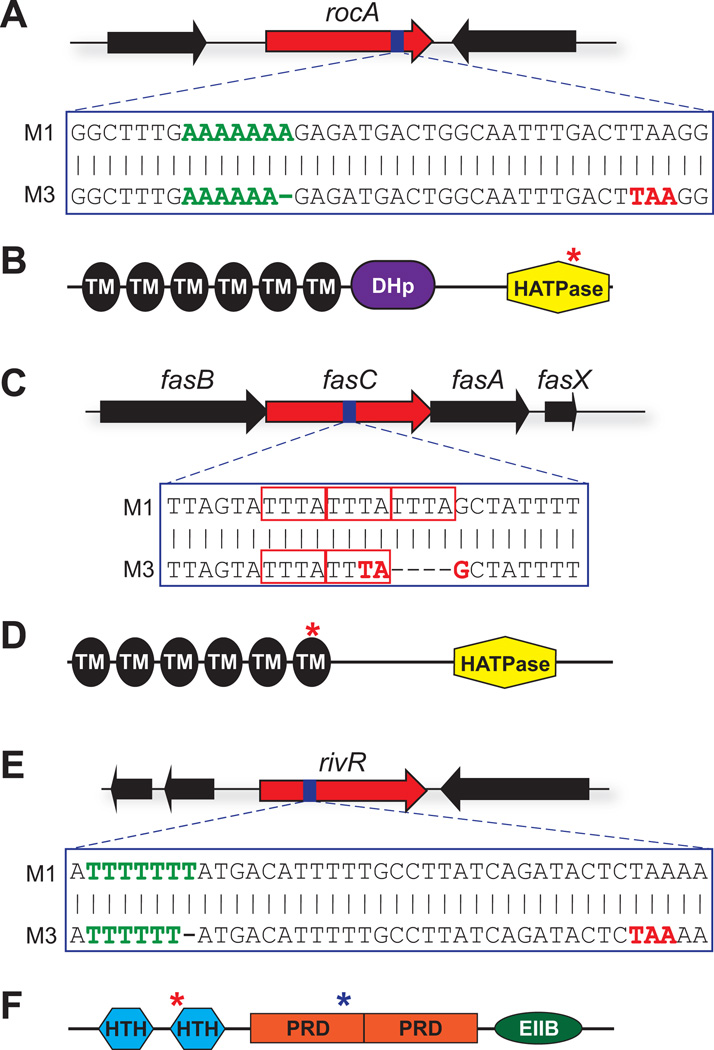
Figure 4. Serotype M3 GAS isolates harbor mutations in the rocA, fasC, and rivR regulator-encoding genes.
(A) M3 isolates have a 1 bp deletion in rocA. Shown is a schematic of the rocA gene, with the region of the gene that contains the 1 bp deletion in serotype M3 isolates being highlighted with blue shading. The nucleotide sequence of this region is shown in a comparison between M1 and M3 isolates. The green nucleotides highlight the homopolymeric tract which contains the M3 GAS deletion, while the red nucleotides highlight the premature start codon which is introduced into the M3 GAS rocA gene due to the deletion. (B) Domain analysis of the RocA protein. Identified domains are: transmembrane domains (TM; black), a dimerization and histidine phosphotransfer domain (DHp; purple), and a histidine-kinase-like catalytic domain (HATPase; yellow). The red asterisk highlights the location of the truncation that occurs in serotype M3 isolates. (C) M3 isolates have a 4 bp deletion in fasC. The red rectangles highlight the three tetra-nucleotide repeat sequences, one of which is deleted in serotype M3 GAS isolates. (D) Domain analysis of the FasC protein. The red asterisk highlights the location of the truncation that occurs in serotype M3 isolates. (E) M3 isolates have a 1 bp deletion in rivR. (F) Domain analysis of the RivR protein. RivR is a member of the Mga-like family of transcriptional regulators, and similar to Mga has helix-turn-helix DNA-binding motifs (HTH), phosphotransferase system regulatory domains (PRD), and a domain important in oligomerization (EIIB-like). The red asterisk highlights the location of the truncation that occurs in serotype M3 isolates. The blue asterisk highlights the location of the L242P amino acid substitution that occurs in M3 isolates.