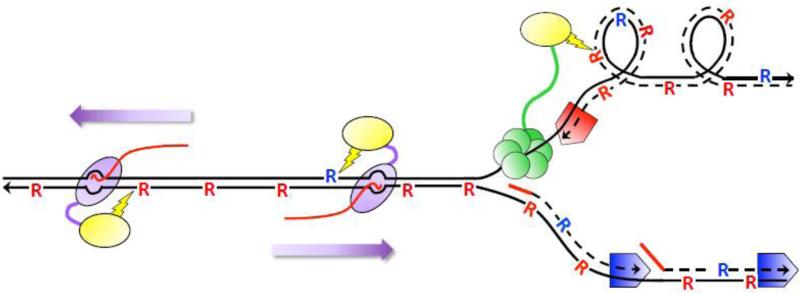
Figure 2.
Ribonucleotide-dependent deletions during replication and transcription in the absence of RNase H2. Black lines are DNA and arrowheads designate 3’-OH ends. Dotted lines are DNA synthesized during replication and solid red lines are RNA primers for DNA synthesis. Red and blue pentagons correspond to Pol ε and Pol δ, respectively. “R” corresponds to ribonucleotides; those inserted by Pol ε and Pol δ are red and blue, respectively. The red line trailing RNAP is the RNA transcript. Top1 (yellow oval) is tethered to components of the replication (CMG helicase in green) and transcription machineries (purple oval moving in the direction of the purple arrow) to relieve supercoils formed during each. During replication, supercoils form on the leading strand of replication and Top1 incision generates deletions primarily at ribonucleotides incorporated by Pol ε. During transcription, deletions reflect incision at ribonucleotides located on the NTS, which can be inserted by either Pol ε or Pol δ.