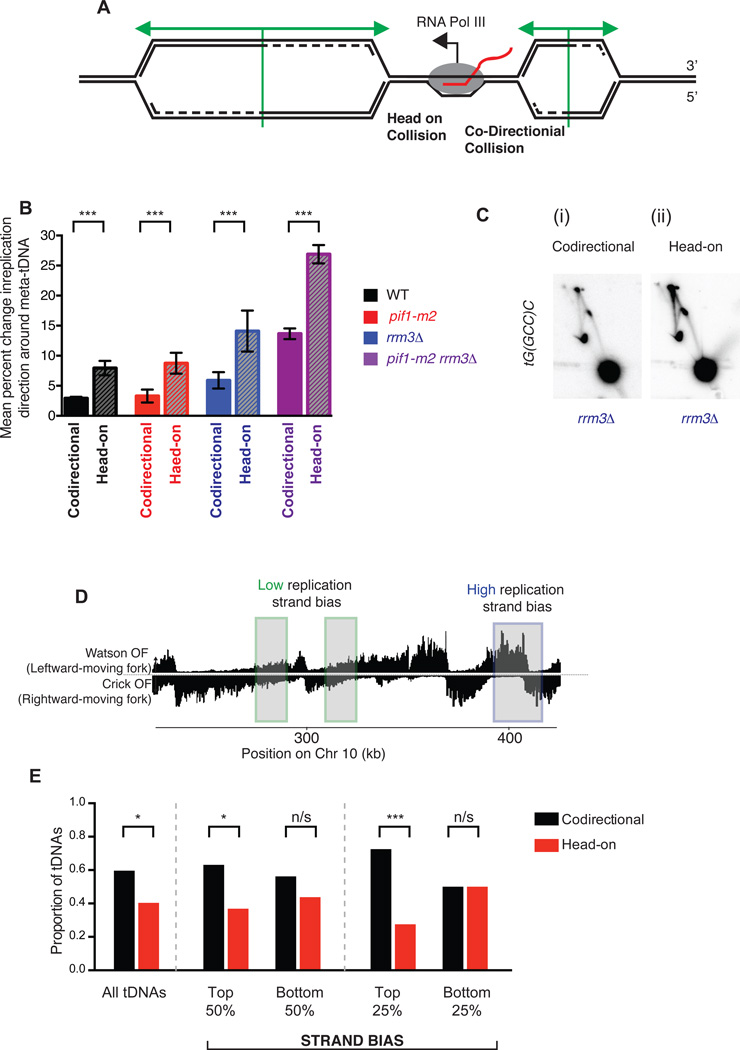
Figure 5. All tDNAs act as replication terminators, but head-on orientation between replication and transcription machinery increases fork arrest.
(A) Schematic of two replication forks approaching a highly transcribed tDNA. The fork moving from left to right will meet the transcribing RNA Polymerase III molecule in a head-on fashion. (B) Grand mean ± SD from three independent experiments of the change in replication direction, interpreted as indicative of replisome arrest, at tDNAs transcribed co-directionally or head-on relative to the predominant direction in which they are replicated (see methods). Termination signal was calculated as in Figure 2E. Significance was determined by Monte Carlo resampling; *** indicates a p<0.0001 (C) Neutral-neutral 2-D agarose gel electrophoresis of the plasmid shown in Fig. 3B, but with tG(GCC)C in either the codirectional or head-on orientation as indicated, purified from an asynchronous S. cerevisiae culture. (D) Schematic of chromosomal regions of high (blue) and low (green) replication strand bias. (E) Bar plot indicating the proportion of tDNAs oriented head-on or codirectionally relative to replication, separated into bins (above or below the median strand bias for the 275 nuclear tDNAs) as indicated by strand bias as shown in D. All tDNAs (n=275), high and low strand bias (n=137) and top and bottom quartiles (n=68) were calculated and p-values for cumulative binomial; *** indicates a p<0.0001; * indicates 0.0001 < p < 0.05; n/s indicates p>0.05.