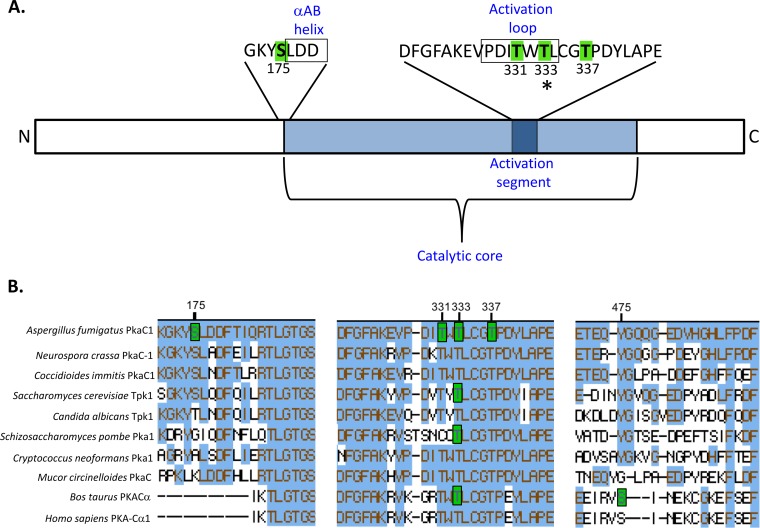
FIG 1 .
Multiple sites of phosphorylation identified in PkaC1 by mass spectrometry. (A) Diagram showing locations of phosphorylated sites within the PkaC1 protein. Residues highlighted in green were identified by LC-MS/MS as phosphorylated. Serine 175 is located immediately outside the conserved catalytic core and adjacent to a region with homology to the αAB helix (boxed) identified in the S. cerevisiae Tpk1 crystal structure. Threonine residues at positions 331, 333, and 337 are located in the conserved activation segment of the catalytic core containing residues essential for catalytic activity of PKA. T331 and T333 are located within a subdomain of this segment known as the activation loop (boxed). The asterisk at T333 indicates the conservation in phosphorylation of this residue in other species. (B) Clustal W alignment of phosphorylated regions of PKA catalytic subunits of selected fungal and mammalian species. Amino acids highlighted in blue indicate their conservation in relation to A. fumigatus PkaC1. Amino acids highlighted in green indicate residues that have been experimentally determined to undergo phosphorylation in the associated organism. Numbering of the residues showing the respective phosphorylation is based on the A. fumigatus protein. Of the two phosphorylated sites identified in mammalian PKA, only one site corresponding to residue T333 is conserved in A. fumigatus. S175 is conserved among some fungal species but not in mammalian enzymes. T333 and T337 are conserved in all species analyzed, while T331 is conserved in all except S. pombe.