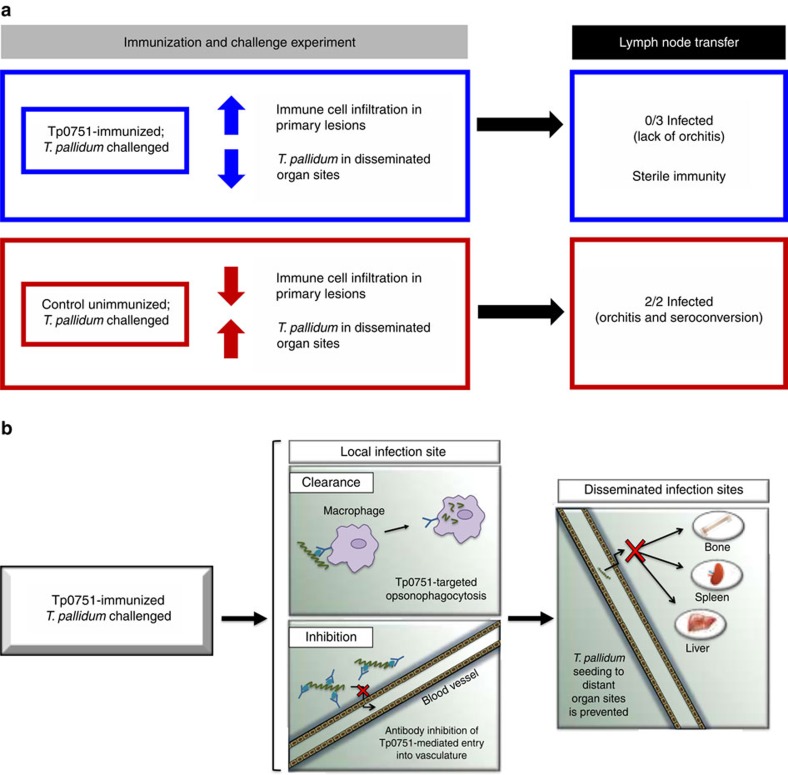
Figure 5. Summary of key findings and proposed mechanisms.
(a) Summary of key findings. Tp0751 immunization promotes cellular infiltration into primary lesions and inhibits T. pallidum dissemination to distant organ sites. Lymph node transfer from Tp0751-immunized to naïve animals does not cause T. pallidum infection, confirming sterile immunity. (b) Proposed mechanism for the protection against T. pallidum dissemination conferred by Tp0751 immunization. We propose that Tp0751 immunization induces specific antibody production in primary lesions, facilitating T. pallidum clearance via macrophage opsonophagocytosis. Local Tp0751-specific antibodies would also inhibit T. pallidum bloodstream entry by preventing Tp0751-mediated adhesion to blood vessel components. Collectively, these reactions would prevent T. pallidum from accessing the bloodstream and secondary infection sites.