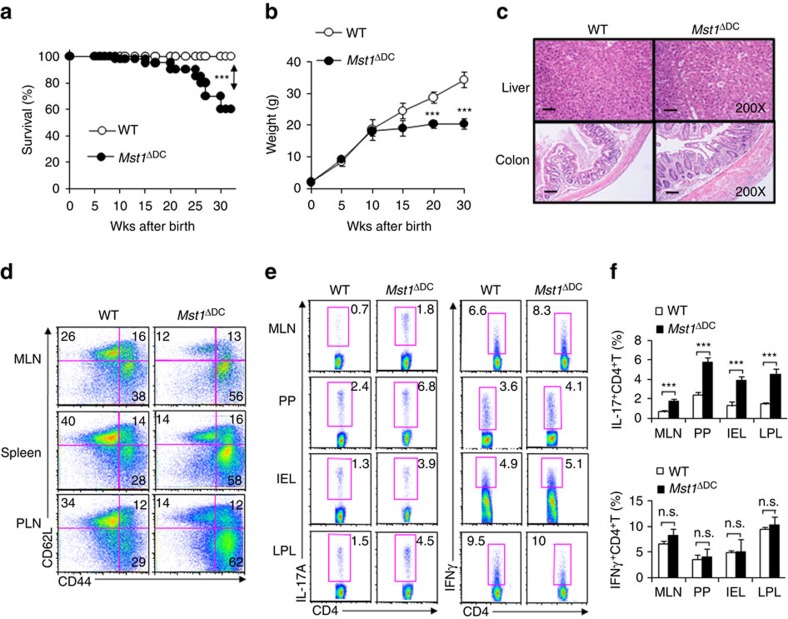
Figure 1. DC MST1 deficiency leads to spontaneous diseases.
(a) Kaplan–Meier plots of WT and Mst1ΔDC mouse survival after birth are shown (n=20). (b) Body weights of the WT and Mst1ΔDC mice after birth are summarized (n=20). (c) H&E staining of hepatic and intestinal tissues from sex- and age-matched WT and Mst1ΔDC mice at 20 weeks after birth is presented. Scale bars, 100 μm. (d) DC MST1 deficiency leads to more CD44highCD62Llow cells among CD4+T cells than WT control mice at 20 weeks after birth. Gating strategies for determining the percentage of CD4+TCR+CD44highCD62Llow cells are showed in Supplementary Fig. 4C. Intracellular IL-17A and IFN-γ expression of CD4+T cells isolated from MLN, PP, IEL and LPL in WT and Mst1ΔDC mice with a typical figure displayed (e) and the frequencies of positive cells summarized (f). Data are representative of three to four independent experiments (mean±s.d.; n=4). ***P<0.001, compared with the indicated groups. n.s., not significant. P-values were determined using Student's t-tests.